Table 1.
Genes involved in each disease and their functions ( = uniquely downregulated, ↓=downregulated,
= uniquely downregulated, ↓=downregulated,  =uniquely upregulated and ↑=upregulated)
=uniquely upregulated and ↑=upregulated)
| Disease | Genes | Functions/pathways |
|---|---|---|
| AQM |
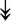 CASQ1, CASQ1, 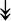 ANK1, ANK1, 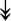 CAPN3 CAPN3 |
SR-related proteins: indicative of SR size and Ca2+ storage. |
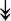 CACNA1S, ↓CACNB1, ↓CACNG1 CACNA1S, ↓CACNB1, ↓CACNG1 |
Serve as gates for Ca2+ from the t-tubule to SR needed to activate RyR1. Activated RyR1 allows release of Ca2+ into the sarcoplasm. | |
| ALS |
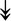 ACTA1, ACTA1, 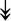 TNNI2, TNNI2, 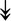 TNNC1, TNNC1, 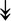 TNNC2, TNNC2, 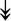 TNNT1, TNNT1, 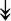 NEB, ↓TPM-1/2/3 NEB, ↓TPM-1/2/3 |
Actin-related proteins: tropomyosins, which wrap around actin, prevent actin–myosin interaction. Troponins serve as binding sites on tropomyosin for Ca2+ and help strip tropomyosin from actin to allow myosin to interact with actin. |
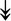 MYH11, MYH11, 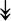 MYL1, MYL1, 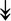 MYL2, MYL2, 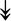 MYLPF, MYLPF, 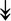 TTN, ↓MYH2, ↓MYH7, ↓MYOM1 TTN, ↓MYH2, ↓MYH7, ↓MYOM1 |
Myosin-related proteins: myosin is comprised of heavy and light chains. Titin binds to the myosin, providing muscle integrity during its contraction and relaxation. Myomesins are responsible for anchoring myosin to titin. | |
| DM |
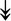 PQBP1, PQBP1, 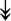 USP39, USP39, 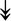 SNW1, SNW1, 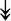 LSM4, LSM4,  PRPF31, PRPF31,  PRPF19, PRPF19,  NAA38, NAA38,  XAB2, XAB2,  SNRPD2, SNRPD2,  U2AF1, U2AF1,  PRPF4, PRPF4,  RBM8A RBM8A |
Responsible for splicing of pre-mRNA. |
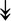 RSL24D1, RSL24D1, 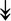 RPL11, RPL11, 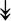 RPL37, RPL37, 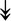 RPL37A, RPL37A,  RPL36A, RPL36A,  RPS8, RPS8,  RPS20, RPS20,  RPL23 RPL23 |
Large and small ribosome subunits. | |
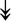 GANAB, GANAB, 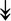 LMAN1, LMAN1, 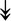 PRKCSH, PRKCSH, 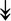 RRBP1, RRBP1,  CALR, CALR,  EIF2AK2, ↑EIF2AK1 EIF2AK2, ↑EIF2AK1 |
Proteins related to protein processing in ER. | |
 UBE4B, UBE4B,  PRPF19, PRPF19,  ANAPC5, ANAPC5,  TCEB2, TCEB2,  UBE2E1, UBE2E1,  UBE2M UBE2M |
Responsible for proper degradation of incorrectly folded proteins. | |
| PM |
 HLA-A/B/C/F/G, ↑HLA-DR/DP/DQ/DM HLA-A/B/C/F/G, ↑HLA-DR/DP/DQ/DM |
MHC-I and MHC-II related proteins: MHC-I and MHC-II proteins are immune response proteins responsible for displaying antigen fragments. |
 CXCL13, CXCL13,  CXCR6, CXCR6,  GNB5, GNB5,  DOCK2, DOCK2,  CXCL9, CXCL9,  RAC2, RAC2,  CCL4, CCL4,  CCL13, CCL13,  CCL18, CCL18,  XCL1 XCL1 |
Chemokines, responsible for signaling immune cells. | |
 ITGA6, ITGA6,  ITGA4, ITGA4,  SIGLEC1, SIGLEC1,  COL4A6, COL4A6,  ITGB7 ITGB7 |
Proteins involved in cell adhesion molecules, focal adhesion and ECM receptor interaction, all of which aid leukocyte trafficking and migration. |
