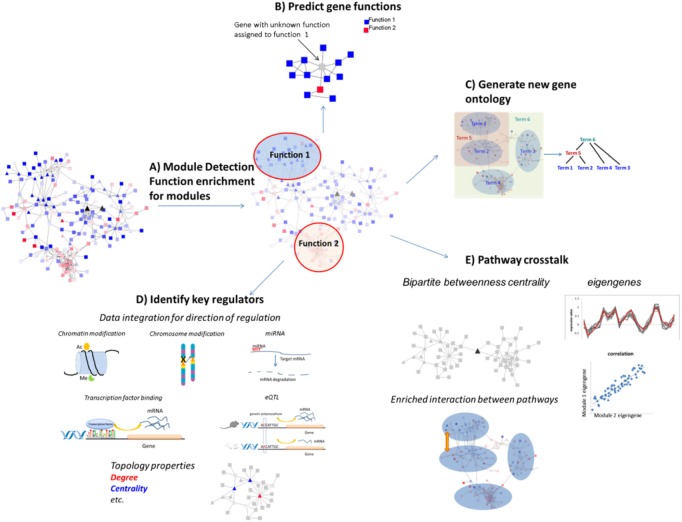
Figure 6.
Network interrogation. (A) Densely connected subnetworks (modules) are detected, and enriched functions of those modules are detected. (B) Genes with unknown function (gray) can be annotated based on the function of its neighbors in the network or the functions of the genes in the same module. (C) New gene ontologies can be generated by analyzing the hierarchical organization of gene clusters. (D) Multiple data types can be integrated to help infer the direction of regulation and identify key regulators based on their network topological features. (E) Crosstalks between pathways can be studied by extracting eigengenes or analyzing enriched interactions between networks. Key regulators for pathway crosstalk can also be identified based on their between-module topology properties.