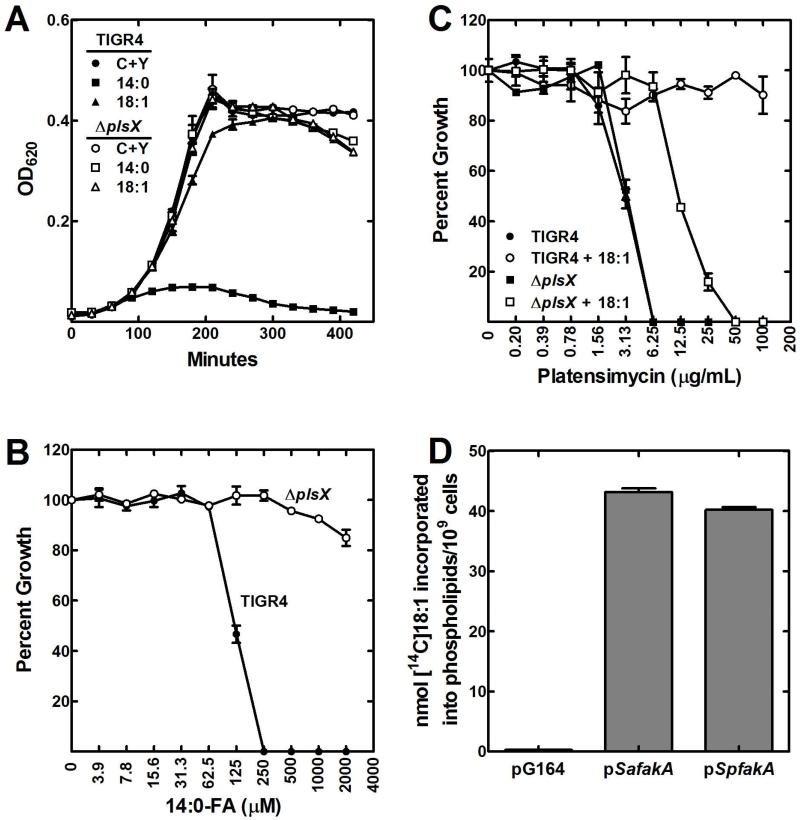
Fig. 2.
Growth phenotypes of S. pneumoniae strain MDJ01 ΔplsX).
A. Growth of S. pneumoniae strains TIGR4 (wild-type) and MDJ01 (ΔplsX) in CY/BSA medium supplemented with either 1 mM 18:1Δ9 or 500 μM 14:0 fatty acids.
B. Determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration of 14:0 fatty acid for wild-type strain TIGR4 and MDJ01 (ΔplsX) grown in CY/BSA (C+Y) medium.
C. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration of platensimycin in wild-type strain TIGR4 and MDJ01 (ΔplsX) grown in CY/BSA medium with and without a 1 mM 18:1Δ9 supplement. Platensimycin is a potent inhibitor of the elongation condensing enzyme (FabF) of FASII.
D. The S. pneumoniae fakA (SP0443) gene encodes a functional fatty acid kinase. Unlike in S. aureus, S. pneumoniae fakA is an essential gene. Therefore its function as a fatty acid kinase in fatty acid uptake was evaluated by expressing SpFakA in a S. aureus ΔfakA strain. Like its S. aureus counterpart, SpFakA expression restored [14C]oleate (18:1Δ9) incorporation into phospholipid when expressed in a ΔfakA background.