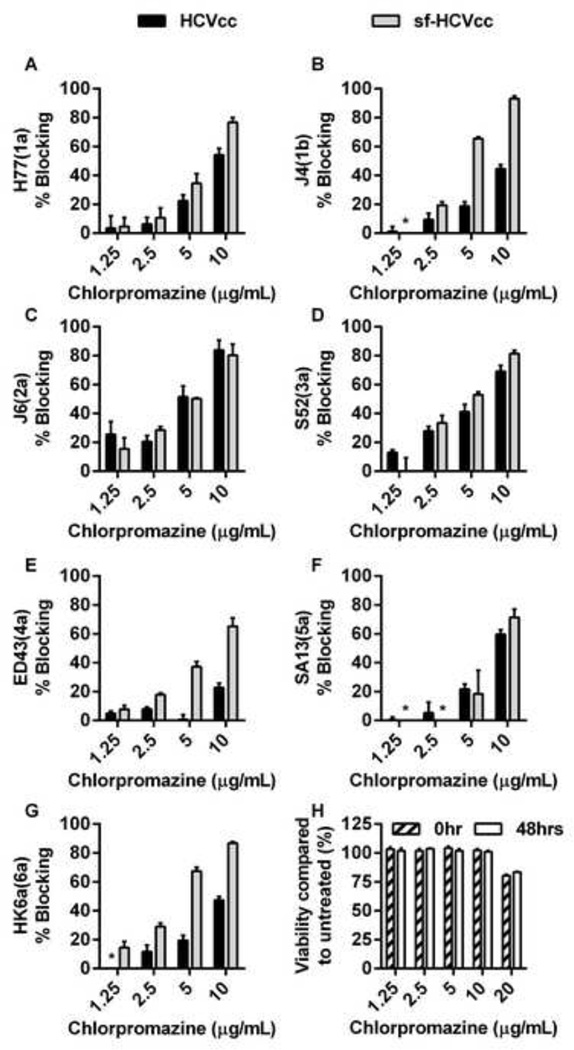
Figure 11. Effect of chlorpromazine treatment on HCVcc and sf-HCVcc entry.
(A-G) Chlorpromazine was diluted in DMEM + 10% FBS to the concentrations indicated and then added to Huh7.5 cells, plated the previous day onto poly-D-lysine coated 96-well plates, and incubated for 30 minutes. HCVcc (black bars) were diluted in DMEM + 10% FBS and sf-HCVcc (grey bars) were diluted in AEM + 10% FBS and added to cultures. After 6 hours incubation, chlorpromazine-virus mixes were removed and DMEM + 10% FBS was added. Cells were fixed 48 hours post infection and stained, and the number of single HCV NS5A positive cells per well was determined by automated counting as described in Materials and Methods. The HCV Core-E2 sequences of all virus stocks used were determined by direct sequencing. Sequences were identical for HCVcc and sf-HCVcc of the same recombinant. Compared to the plasmid sequence, H77(1a) viruses had acquired amino acid change I348S and J4(1b) had acquired amino acid change V710L, both estimated to be present in the majority of viral genomes. The % blocking was calculated by relating counts of experimental wells to the mean count of six replicate wells with untreated control virus. Data points are means of three replicates with SEM (error bars). (H) Chlorpromazine was diluted in DMEM + 10% FBS to the concentrations indicated and then added to Huh 7.5 cells, plated the previous day in poly-D-lysine coated 96-well plates. Cells were incubated for 6 hours before chlorpromazine was removed and DMEM + 10% FBS was added. A cell viability assay was carried out on cells incubated for 6 hours with chlorpromazine and on control cultures as described in Materials and Methods (0 hrs post treatment; dashed bars). An additional cell viability assay was carried out on chlorpromazine treated- and control cultures 48 hours post treatment (white bars). The % viability was calculated by relating absorbance at 490 nm determined for chlorpromazine treated cultures to the mean absorbance of three replicate untreated cultures. Bars represent the means of three replicates with SEM. *, values <0.