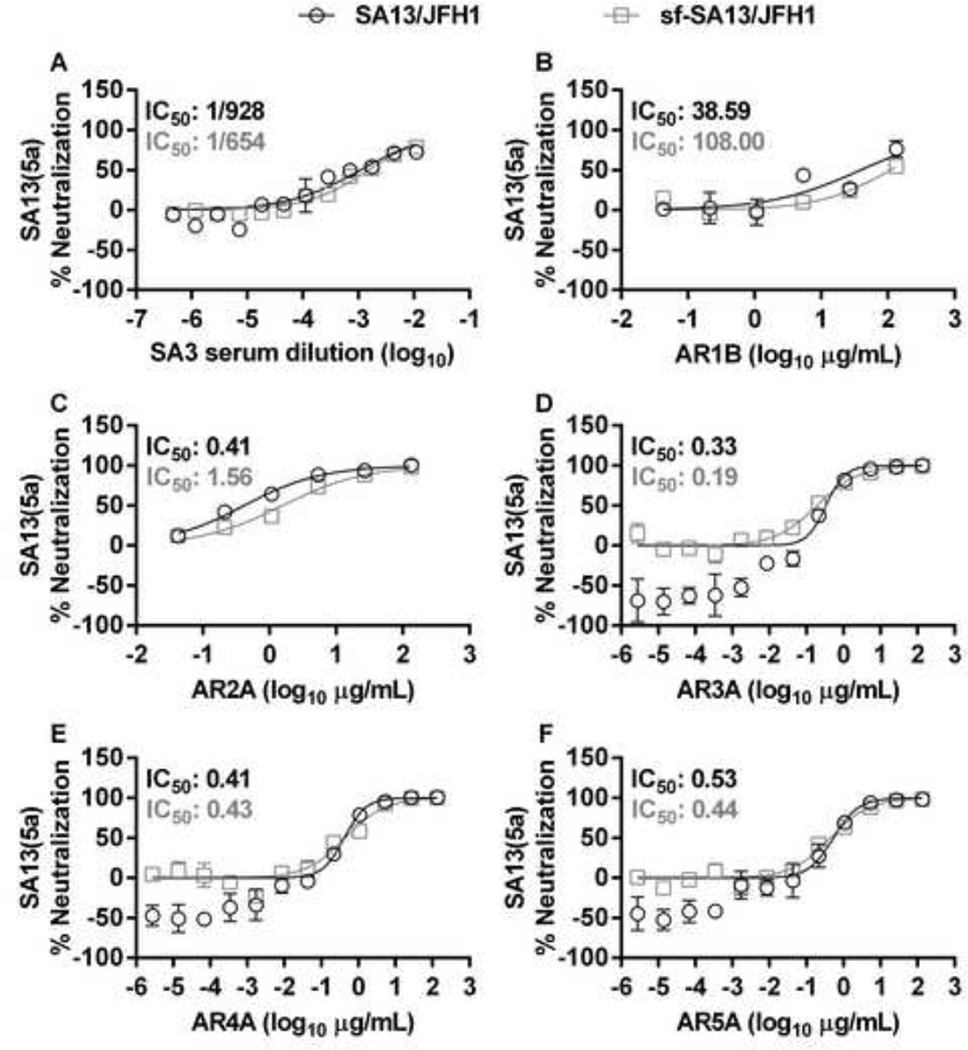
Figure 13. SA13(5a) and sf-SA13(5a) show similar susceptibility to genotype 5a patient serum and human monoclonal antibodies.
(A) Genotype 5a chronic phase serum SA3 or (B-F) monoclonal antibodies AR1B and AR2A-5A were diluted in DMEM + 10% FBS as indicated. HCVcc (black circles) were diluted in DMEM + 10% FBS and sf-HCVcc (grey squares) were diluted in AEM + 10% FBS, mixed with SA3 serum, AR1B or AR2A-5A antibody dilutions and incubated 1 hour at 37°C. Virus-serum or virus-antibody mixes were added to Huh7.5 cells, plated the previous day in poly-D-lysine coated 96 well plates. After 6 hours incubation, virus-serum or virus-antibody mixes were removed and DMEM + 10% FBS was added. Cells were fixed 48 hours post infection and stained, and the number of single HCV NS5A positive cells per well was determined by automated counting as described in Materials and Methods. The % neutralization was calculated by relating counts of experimental wells to the mean count of six replicate wells with untreated control virus. Data points are means of three replicates with SEM (error bars). Following logarithmic transformation of X-values, variable-slope sigmoidal dose-response curves were fitted [Y = Bottom+(Top-Bottom)/(1 + 10(Log10EC50-X)×HillSlope)]. “Bottom” was constrained to “0” for all curves. “Top” was constrained to “100” for all curves. Median inhibitory concentrations (IC50) were calculated (black for HCVcc and grey for sf-HCVcc).