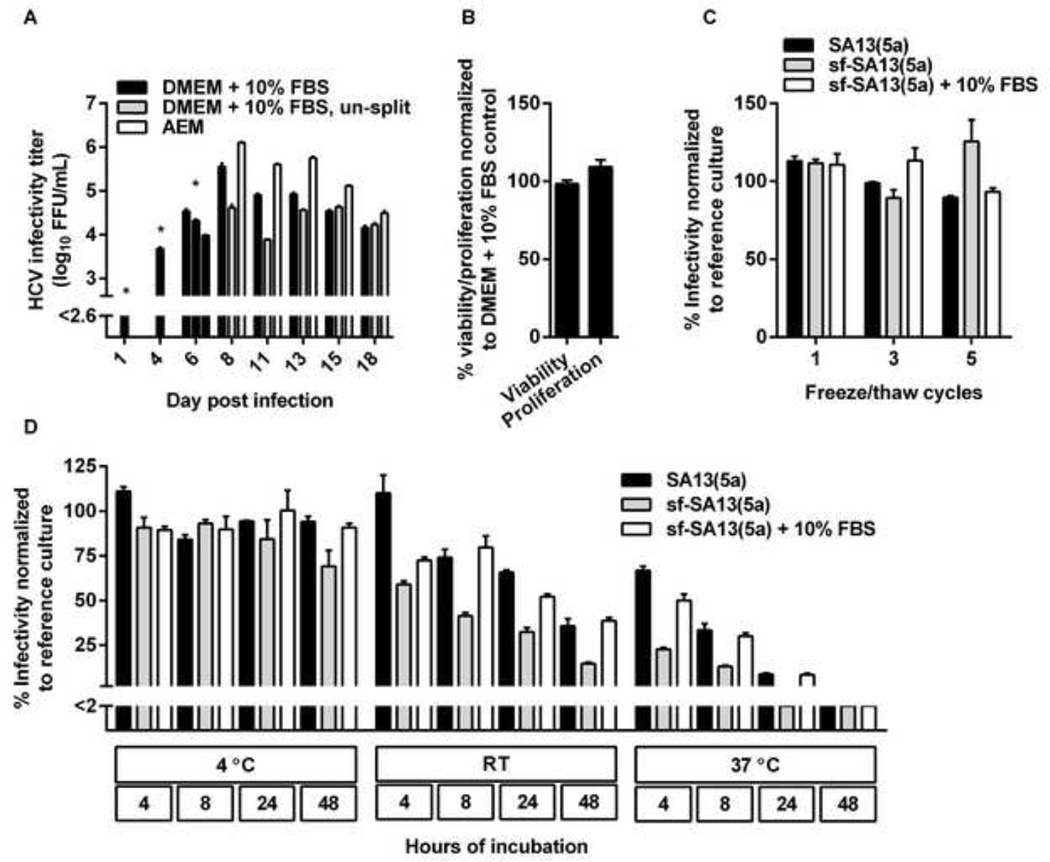
Figure 3. Increased infectivity titers of serum-free cell cultures were not due to reduced cell-splitting, changes in cell viability or proliferation, or increased viral stability.
(A) AEM cultures produced higher infectivity titers than DMEM + 10% FBS cultures handled similarly and DMEM + 10% FBS control cultures. Huh7.5 cells were infected with the SA13(5a) JFH1-based Core-NS2 recombinant in DMEM + 10% FBS for 3 hours at an MOI of 0.003. On day 4 post-infection, cells were split into three replicate cultures. Following day 6 post infection, when ~80% of culture cells were infected, as determined by HCV NS5A immunostaining, one replicate culture was maintained in DMEM + 10% FBS and split every 2–3 days, another replicate culture was maintained in DMEM + 10% FBS without being split, while the third replicate culture was maintained in AEM without being split. At the indicated days post infection, supernatants were collected. Supernatant HCVcc infectivity titers are shown as means of 3 replicates with standard error of the mean (SEM). The lower limit of detection in the experiment shown was up to 2.6 log10 FFU/ml, indicated by y-axis break. * The culture originally infected with SA13(5a) was first split into three replicates at day 4 post infection; thus, on day 1 and 4 post infection only one infectivity titer is shown. On day 6, DMEM + 10% FBS supernatants were harvested from the three replicate cultures; subsequently cultures were maintained in the different growth media indicated. (B) AEM cultures showed similar viability and proliferation as DMEM + 10% FBS cultures. Cell viability or proliferation of Huh7.5 cells cultured for 48 hours in AEM versus DMEM + 10% FBS was determined as described in Materials and Methods. The % viability/proliferation was calculated by relating absorbance at 490 nm (viability) or 450 nm (proliferation) determined for AEM cultures to the mean absorbance of 10 replicate DMEM + 10% FBS cultures. Bars represent the means of 10 replicates with SEM. (C) sf-HCVcc and HCVcc showed similar freeze-thaw stability. SA13(5a) diluted 1:100 in DMEM + 10% FBS or sf-SA13(5a) diluted 1:100 in either AEM or AEM + 10% FBS were exposed to up to 5 freeze/thaw cycles. Samples were thawn at room temperature and frozen at −80°C. After the indicated number of cycles, infectivity titers were determined as described in Materials and Methods. The % infectivity was calculated by relating the infectivity titer of each sample to the mean titer of a reference sample of the same stock, which had been stored at −80°C. Bars represent the means of three replicates with SEM. (D) sf-HCVcc showed decreased stability under temperature stress. SA13(5a) diluted 1:100 in DMEM + 10% FBS or sf-SA13(5a) diluted 1:100 in either AEM or AEM + 10% FBS were incubated at 4°C, room temperature (RT) or 37°C for 4 to 48 hours as indicated. Infectivity titers were determined as described in Materials and Methods. The % infectivity was calculated by relating the infectivity titer of each sample to the mean titer of a reference sample of the same stock, which had been stored at −80°C. Bars represent the means of three replicates with SEM. The lower limit of detection in the experiment shown was up to 2%, indicated by y-axis break.