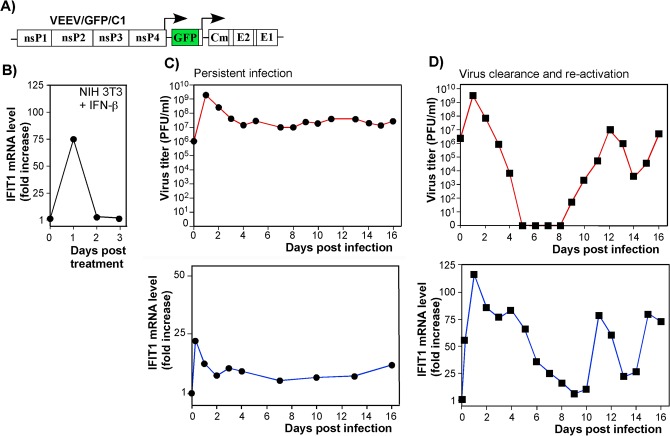
Fig 6. IFIT1 is expressed via IFN-dependent and alphavirus replication-dependent pathways.
(A) The schematic representation of VEEV TC-83-based recombinant virus genome (VEEV/GFP/C1) containing mutations in the capsid-specific NLS. (B) The profile of IFIT1 induction in the NIH 3T3 cells treated for 24 h with IFN-β (500 IU/ml) and then incubated in IFN-free media. (C) IFN-α/βR-/- MEFs were infected with VEEV/GFP/C1 at an MOI of 20 PFU/cell. Media were replaced at the indicated time points, and cells were harvested for RNA isolation and analysis. Panels represent titers of the virus and IFIT1 mRNA accumulation profiles. (D) NIH 3T3 cells were infected with VEEV/GFP/C1 at an MOI of 20 PFU/cell. As in the experiment presented in panel (C), media were replaced at the indicated times post infection, and RNAs were isolated from the cells. Panels represent titers of the virus and IFIT1 mRNA accumulation profiles. Two independent RNA samples were prepared for each time point for VEEV/GFP/C1-infected cells and three RNA samples for IFN-β-treated cells.