Fig. 2.
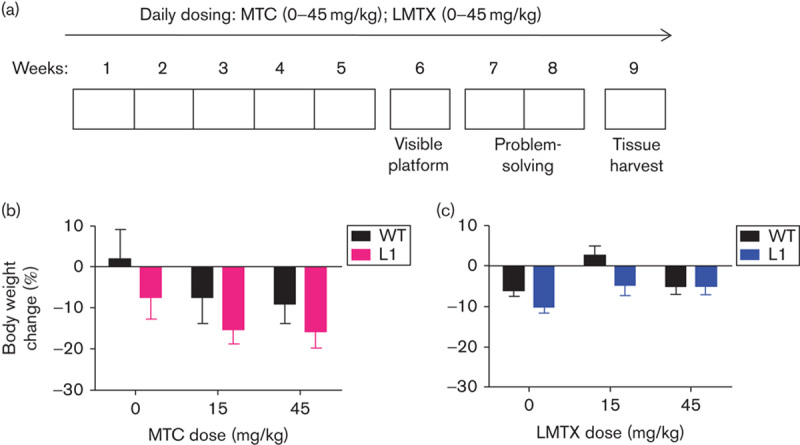
Experimental design adopted in the problem-solving task, and drug effects on body weight. (a) L1 and WT mice were orally treated for 5 weeks (Monday to Friday) with either vehicle, MTC or LMTX (15 and 45 mg/kg) and then tested in the water maze. The paradigm included visible platform training (week 6: 4 days), followed by training to criterion in three spatial problems (weeks 7 and 8) with continuing drug exposure. Brain tissue was collected during week 9. Effects of (b) MTC and (c) LMTX (in this case LMTM) on body weight in L1 and WT mice are shown. Body weight is expressed as the mean percentage change over 8 weeks relative to the start of treatment. Although there were some weight losses relative to pretreatment, drug exposure did not differ from vehicle for either genotype. The 45 mg/kg doses are equivalent to 35.1 mg MT/kg and 26.7 mg MT/kg for MTC and LMTM, respectively. Values are expressed as mean±SE. L1, Line 1; LMTX, leucomethylthioninium salt; MT, methylthioninium; MTC, methylthioninium chloride; WT, wild type.
