Figure 1.
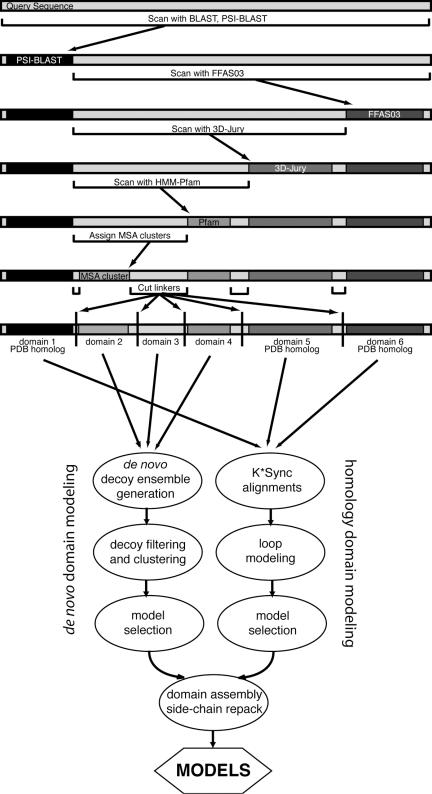
Ginzu domain parsing hierarchy and modeling protocol. The query sequence is scanned for matches to known structures and regions that are likely to be domains. Sections that are not covered but are large enough to be a domain (at least 50 residues) are passed on as input for the next step. The order is based on the relative accuracy of each step. Homologous structure searches are performed first, followed by a search against Pfam-A and then parsing based on MSA sequence clusters. Boundaries are assigned so that putative domains without homologous structures are within size limits accessible to the Rosetta de novo protocol. Regions that are homologous to sequences with known structures are used for comparative modeling. Matches to Pfam-A, MSA cluster domains and remaining uncovered regions of sufficient size are subjected to de novo structure prediction. Domain models are assembled into a full model in the last step.