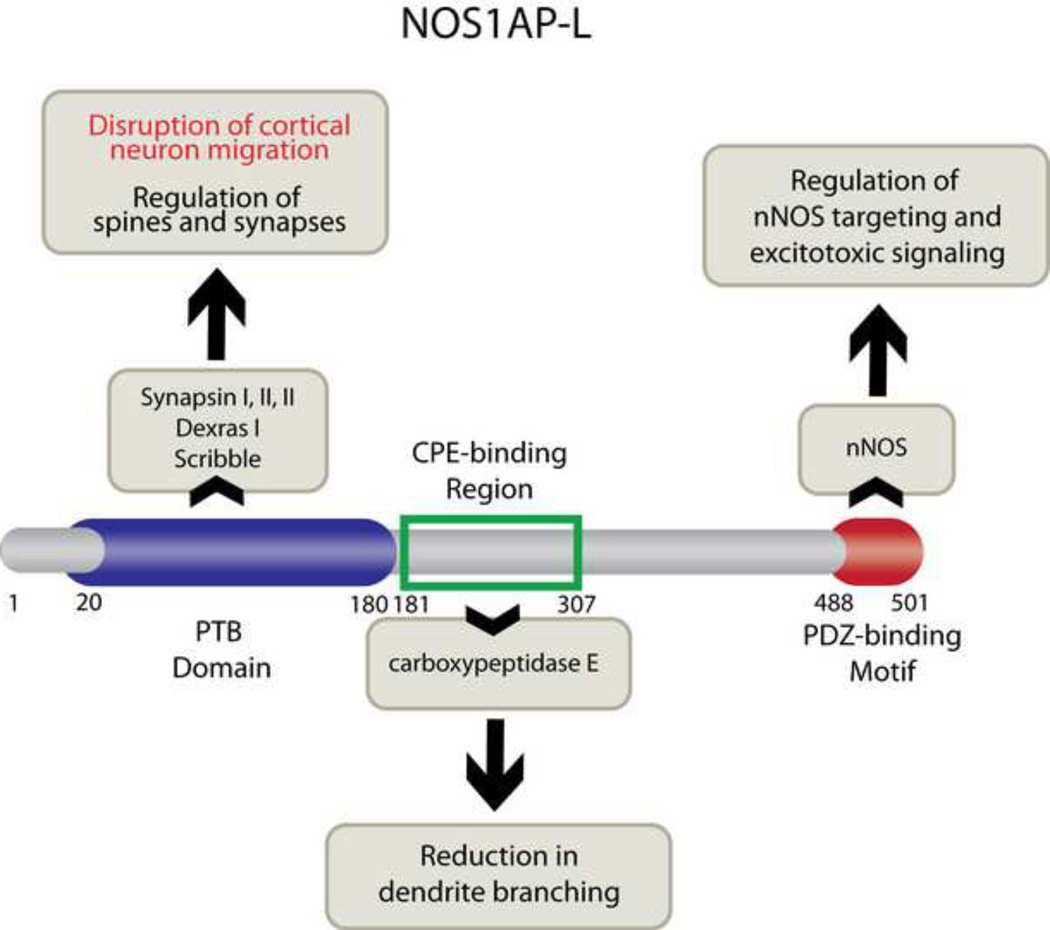
Figure 5. Model of NOS1AP function in neurons.
The long isoform of NOS1AP, NOS1AP-L, contains three domains: the N-terminal phosphotyrosine binding domain (PTB; amino acids 1–180), the carboxypeptidase E (CPE)-binding region (amino acids 181–307), and the C-terminal PDZ-binding motif (amino acids 488–501). The PTB domain is responsible for regulating cortical neuron migration (data presented in this manuscript) and binds to synapsins I, II, III (11), Dexras, (10) and Scribble (12). The CPE-binding region is responsible for NOS1AP effects on dendrite branching (13). The PDZ-binding motif binds to nNOS (also known as NOS1), competes with PSD-95 for nNOS binding, and reduces NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity (8, 75).