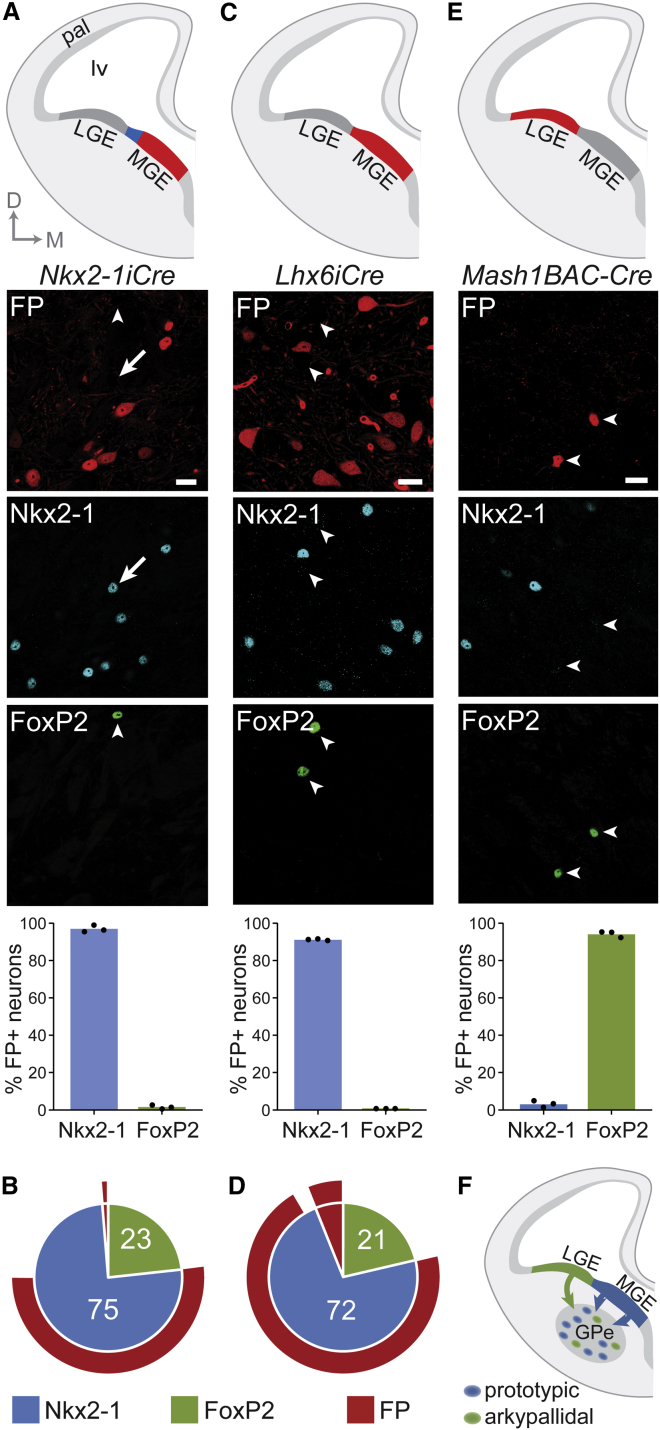
Figure 3.
Arkypallidal and Prototypic GPe Neurons Have Distinct Embryonic Lineages
(A, C, and E) Immunofluorescence labeling and marker expression profiles in three lines of mice used for fate mapping of GPe neurons (FP, fluorescent protein; pseudocolored red). These mice report neurons derived from different embryonic progenitor domains; the regions of the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE) or lateral/caudal ganglionic eminences (LGE/CGE) reported by each mouse line are highlighted in red in the top schematics of embryonic brain. D, dorsal; M, medial; pal, pallium; lv, lateral ventricle.
(A and B) In Nkx2-1iCre;Z/EG mice, which report most MGE-derived neurons, 97% FP+ neurons co-express Nkx2-1. However, only 68% of Nkx2-1+ neurons were also FP+ (B). Thus, a substantial proportion of Nkx2-1+ neurons are not captured by this mouse line (also see arrow in A), likely those emanating from the dorsal-most region of MGE (blue region in top schematic). FP+ neurons in these mice did not co-express FoxP2 (arrowhead).
(C and D) In Lhx6iCre;RCE mice, which report nearly all MGE-derived neurons, the vast majority of FP+ neurons expressed Nkx2-1, and vice versa. FP+ neurons in these mice did not co-express FoxP2 (arrowheads).
(E) In Mash1BAC-CreER;RCE mice, which report neurons derived from LGE/CGE, the vast majority of FP+ neurons co-expressed FoxP2 (arrowheads), but not Nkx2-1.
(F) Schematic summary of fate-mapping experiments. Arkypallidal (FoxP2+) neurons derive from the LGE/CGE of the embryonic subpallium, whereas prototypic (Nkx2-1+) neurons derive from the MGE.
Scale bars, 20 μm.