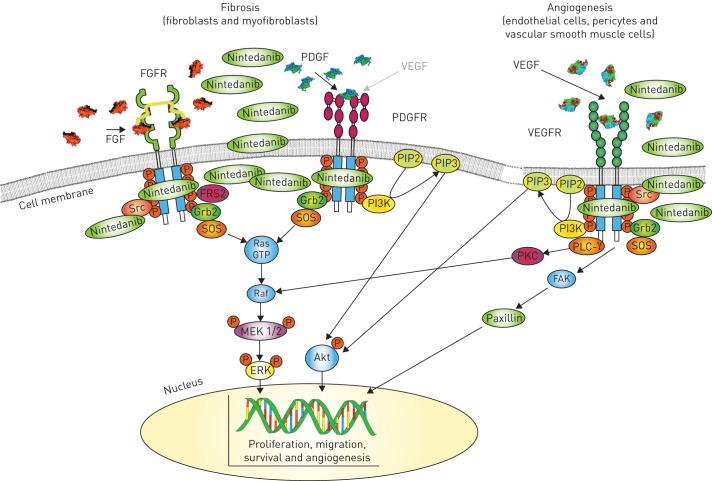
FIGURE 1.
Polypharmacology of nintedanib and the downstream signalling pathways. Nintedanib binds to the intracellular ATP binding pocket of fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs), platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFRs) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs) resulting in blockage of the autophosphorylation of these receptors and the downstream signalling cascades. Nintedanib might exert additional activity by directly blocking non-receptor kinases like Src and Lck (not illustrated). Nintedanib was shown to inhibit PDGFR phosphorylation and subsequent protein kinase B (Akt) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 phosphorylation in lung tissue from mice. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was shown to stimulate angiogenesis via the VEGFR, but also to bind to the PDGFR on fibroblasts, stimulating proliferation. Inhibition by nintedanib ultimately results in reduced proliferation, migration and survival of fibroblasts and, potentially, also to attenuated angiogenesis in the lung. FAK: focal adhesion kinase; FGF: fibroblast growth factor; FRS2: FGFR substrate 2; Grb2: growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; MEK1/2: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2; PDGF: platelet-derived growth factor; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase; PIP2/3: phosphatidylinositol-2/3-phosphate; PKC: protein kinase C; PLC-γ: phospholipase C-γ; SOS: son of sevenless, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor that acts on the Ras GTPases.