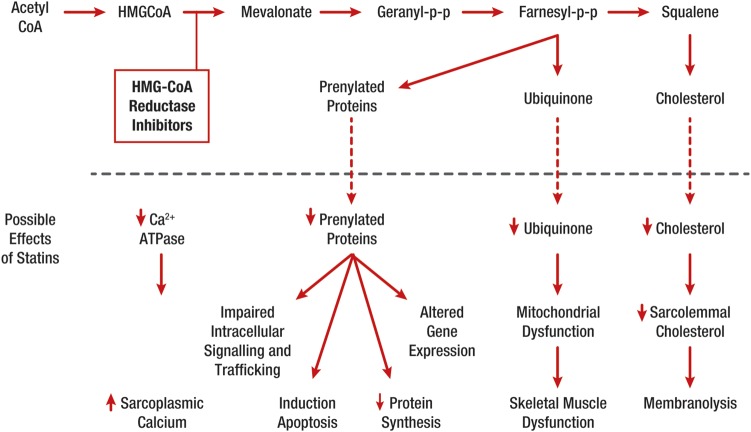
Figure 3.
Effects potentially involved in statin-related muscle injury/symptoms (Reproduced with permission from Needham and Mastaglia 2014).79 A number of statin-mediated effects have been proposed including reduced levels of non-cholesterol end-products of the mevalonate pathway; reduced sarcolemmal and/or sarcoplasmic reticular cholesterol; increased myocellular fat and/or sterols; inhibition of production of prenylated proteins or guanosine triphosphate (GTP)ases; alterations in muscle protein catabolism; decreased myocellular creatine; changes in calcium homeostasis; immune-mediated effects of statins and effects on mitochondrial function—see Figure 4 and Box 4. Ca2+ATPase, calcium ATPase; HMG CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA; PP, pyrophosphate.