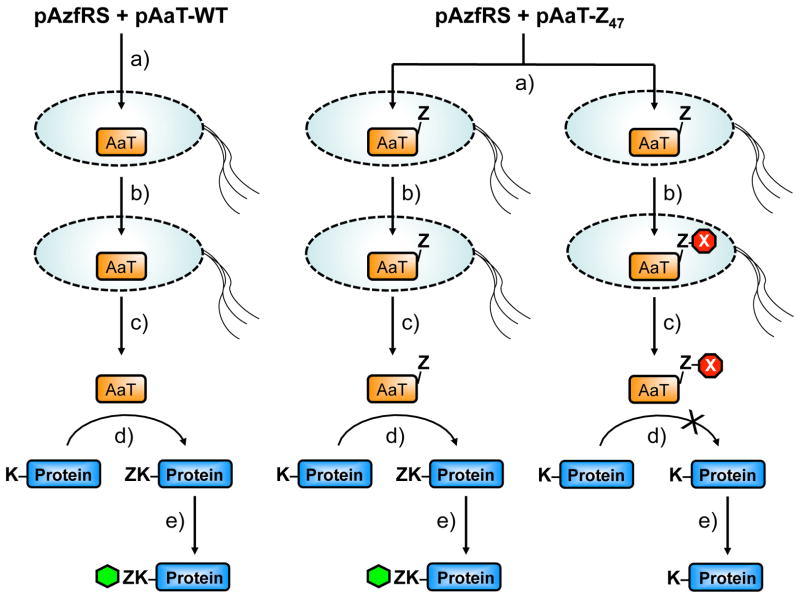
Figure 3.
In Vivo Assay Protocol. Cells are transformed with an AzfRS plasmid and a WT AaT plasmid or a mutant AaT (e.g. Z47) plasmid and subjected to the following conditions: a) AaT production is induced with the addition of Azf and IPTG; b) Cells are pelleted, washed, and reacted with DBCOTMR or DMSO vehicle; c) Cells are grown again after resuspension; d) Cells are lysed and the lysates subjected to an Azf transfer assay using the αS reporter protein, E. coli AzfRS, and AaT; e) Azf transfer levels determined by Cu-catalyzed reaction with a fluorescein alkyne probe. WT control experiments determine the level of transfer activity that should be expected from uninhibited AaT as well as the levels of non-specific binding of the DBCOTMR reagent. Vehicle control experiments determine the level of transfer activity that should be expected from uninhibited AaT mutants (i.e., What is the effect of the Azf mutation alone?). Inhibition by the DBCOTMR reaction is determined by comparing the levels of labeling in the final step to the levels seen in the vehicle control.