Figure 2.
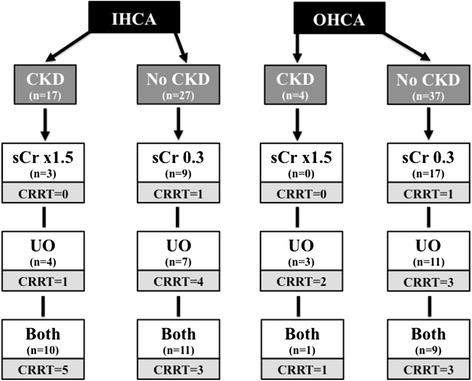
Diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients suffering from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) or in-hospital (IHCA) cardiac arrest. Among patients with previous chronic renal disease (CKD), diagnosis of AKI was initially based on the increase of serum creatinine (sCr) of at least 1.5 times the baseline values or the reduction in daily urine output (UO) or both. Among patients without previous chronic renal disease (No CKD), diagnosis of AKI was initially based on the increase of serum creatinine (sCr) ≥0.3 mg/dL from the baseline value or the reduction of daily urine or both. For each group, the number of patients eventually treated with continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) was reported.
