Figure 3.
SENP6 Antagonizes ID Complex SUMOylation
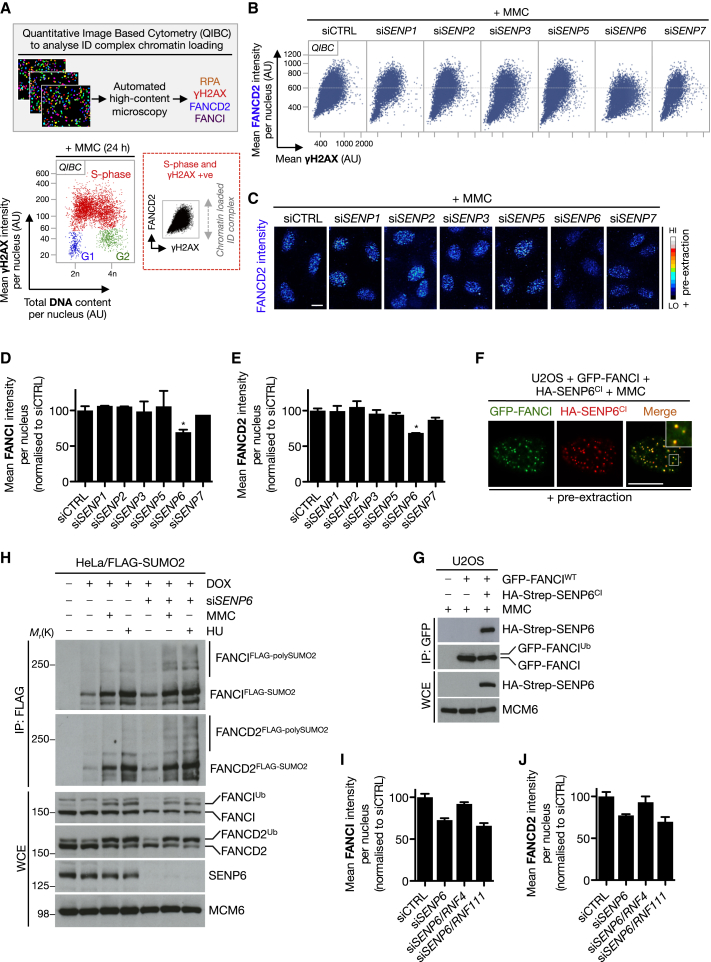
(A) Schematic of QIBC methodology used to analyze ID complex chromatin loading.
(B) U2OS cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs against known SUMO proteases, treated with MMC (0.3 μM) for 24 hr, and then pre-extracted in situ to isolate chromatin bound proteins. Immunostained cells were processed for QIBC as outlined in (A).
(C) Examples from (B) of FANCD2 chromatin-bound levels using QIBC. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
(D) Quantification of mean FANCI chromatin-bound intensity using the same approach as (B). Data represent mean ± SEM from two independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05.
(E) Same as (D), but using FANCD2 antibody.
(F) U2OS cells cotransfected with GFP-FANCI and HA-SENP6CI were treated with MMC (0.3 μM), fixed 4 hr later, and immunostained with HA antibody. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
(G) Same as (F) except cells were subjected to GFP IP followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies.
(H) HeLa/FLAG-SUMO2 cells induced with DOX were treated with SENP6 siRNA and subjected to MMC or HU for 24 hr. Cell lysates were subjected to FLAG IP under denaturing conditions before immunoblotting with indicated antibodies.
(I) U2OS cells transfected with indicated siRNAs were treated with MMC and processed for QIBC. Cells were stained with FANCI antibody and chromatin-bound FANCI was quantified. Data represent mean ± SEM from two independent experiments.
(J) Same as (I) but using FANCD2 antibody.
See also Figure S3.