Figure 6.
FANCI SUMOylation Regulates Activated ID Complex Dosage at Sites of DNA Damage
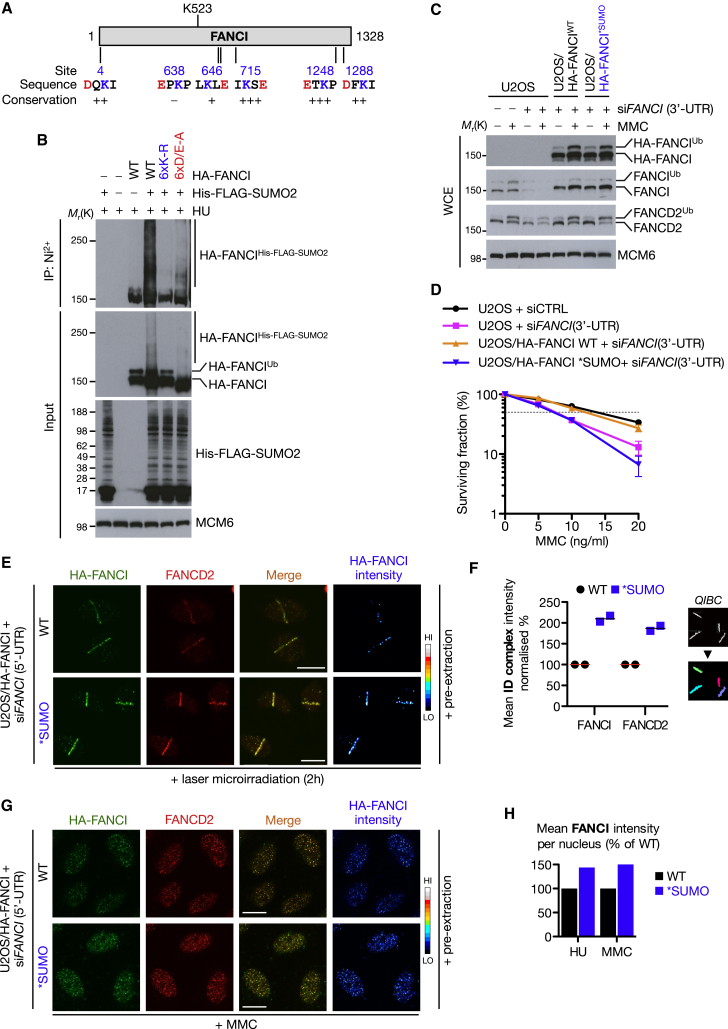
(A) Location and conservation of potential SUMOylation sites in FANCI. Modified lysine residues in consensus SUMOylation motifs are shown in blue with the acidic residue in red.
(B) HeLa cells transfected with HA-FANCI wild-type (WT) or HA-FANCI SUMO-site mutants (6xK-R or 6xD/E-A) together with His-FLAG-SUMO2 were subjected to HU treatment for 24 hr. SUMO conjugates were purified under denaturing conditions using Ni2+ agarose and analyzed by immunoblotting with HA antibody.
(C) Indicated cell lines transfected with control or FANCI (3′UTR) siRNA were treated with MMC for 24 hr and whole-cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies.
(D) Clonogenic survival of indicated U2OS cell lines depleted of endogenous FANCI using the 3′-UTR siRNA where indicated and treated with various doses of MMC. Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments using technical triplicates per datapoint.
(E) U2OS/HA-FANCI WT or ∗SUMO cells transfected with FANCI (5′-UTR) siRNA were subjected to laser microirradiation, pre-extracted, and fixed after 2 hr and then immunostained with HA and FANCD2 antibodies. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
(F) QIBC analysis of normalized mean HA-FANCI and FANCD2 intensities from (E). Data represent mean ± SEM from two independent experiments.
(G) U2OS/HA-FANCI WT or ∗SUMO cells transfected with FANCI (5′-UTR) siRNA were treated with MMC (0.3 μM) for 24 hr and immunostained as in (E). Scale bar represents 10 μm.
(H) U2OS/HA-FANCI cell lines treated as in (G) or with HU were analyzed by QIBC. Mean intensity of chromatin loaded HA-FANCI was normalized to HA-FANCI WT.
See also Figure S6.