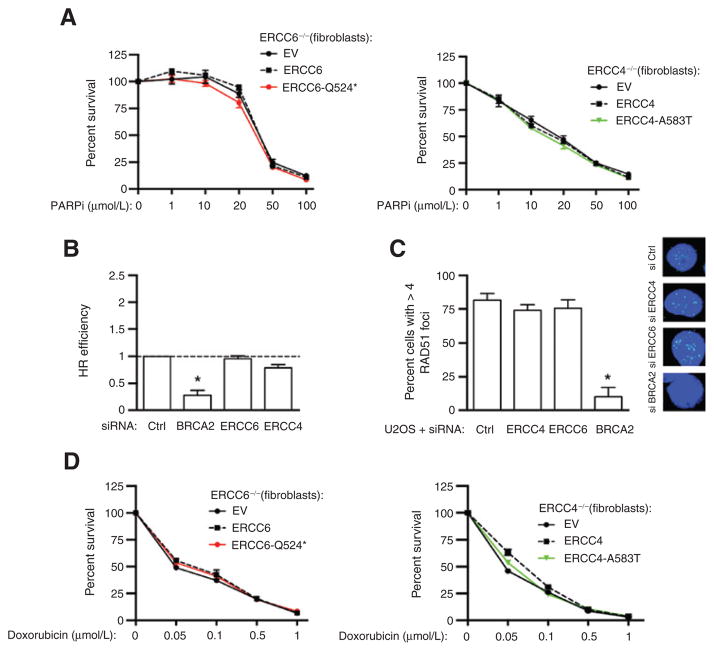
Figure 3.
Inactivation of ERCC6 or ERCC4 does not impair HR efficiency and does not confer sensitivity to rucaparib and doxorubicin. A, addition of wild-type (WT) or mutant ERCC6 in ERCC6-deficient fibroblasts does not affect PARPi (rucaparib) sensitivity (left). Addition of wild-type ERCC4 to ERCC4-deficient fibroblasts does not affect PARPi sensitivity (right). B, siRNA-mediated depletion of ERCC6 or ERCC4 does not significantly affect HR as measured by a DR-GFP recombination assay in U2OS cells. BRCA2 depletion is shown as a positive control. Error bars, ± 1 SEM. Results are representative of three independent experiments. C, siRNA knockdown of ERCC4 or ERCC6 does not affect ionizing radiation-induced RAD51 foci formation in U2OS cells. Cells with ≥4 RAD51 foci were scored as positive. BRCA2-depleted cells are shown as a positive control. Positive cells were quantified 6 hours after irradiation (5 Gy; left plot). For each condition, 100 cells were counted. Error bars, ±1 SEM. Representative micrographs of irradiated cells are shown (right). D, addition of wild-type ERCC6 (black dashes) or mutant protein (red solid line, ERCC6-Q524*) in ERCC6-deficient fibroblasts does not impact sensitivity to doxorubicin (left). Addition of wild-type ERCC4 (black dashes) or mutant ERCC4 (red solid line, ERCC4-A583T) in ERCC4-deficient fibroblasts does not impact sensitivity to doxorubicin (right). Error bars, ± 1 SEM. Results are representative of three independent experiments.