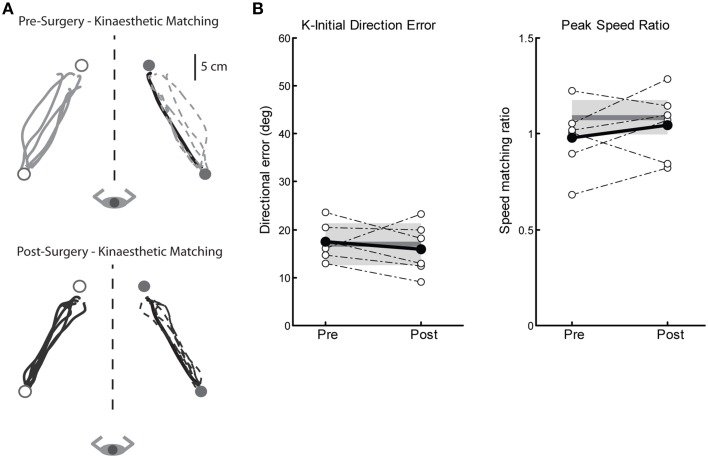
Figure 4.
Exemplar data for the kinaesthetic matching task for a subject before and after left Vim DBS implantation. (A) Pre-surgery kinaesthetic matching behavior (top panel), and post-surgery kinaesthetic matching behavior (bottom panel). (B) Performance on two measures of the kinaesthetic matching task show no impairment in sense of movement direction (initial direction error, left panel) or ability to match the speed of the robot-generated movement (peak speed ratio, right panel). Average control performance (n = 6) is displayed as a solid dark gray line with a gray box representing control subject variability (Standard Deviation). Average patient subject data is presented as a solid black line, with individual subjects as dotted lines. Overall, we observed intact kinaesthetic behavior both pre- (n = 6) and post-surgery (n = 6).