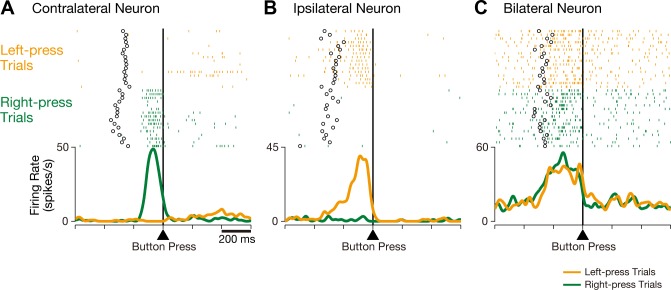
Fig. 2.
Three representative examples of CMAc neurons. A: activity in this CMAc neuron increased when the monkey executed a button press with the contralateral (right) hand but not with the ipsilateral (left) hand. B: activity in this CMAc neuron increased when the monkey executed a button press with the ipsilateral (left) hand but not with the contralateral (right) hand. C: activity in this CMAc neuron increased when the monkey executed a button press with either the contralateral or ipsilateral hand. Rasters and mean spike density functions (smoothed using a Gaussian kernel; σ = 10 ms) indicate activity during right-press trials (green) and left-press trials (orange), and the ordinate represents the instantaneous firing rate (in spikes/s). Neuronal activity is aligned with the button press, open circles indicate the time of onset for the go signal, and the tick marks on the horizontal axis are placed at 200-ms intervals.