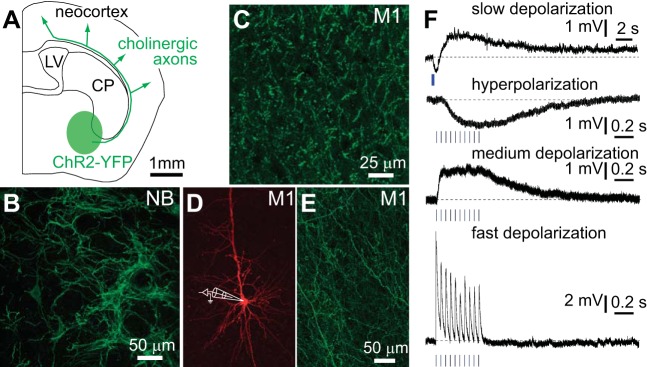
Fig. 1.
Stimulation of cholinergic axons evokes 4 responses in pyramidal neurons. A: schematic of a coronal slice illustrating the expression of channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2)-yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) in cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain and their axonal projections to neocortex. CP, caudate putamen; LV, lateral ventricle. B: image of ChR2-YFP-labeled neurons in nucleus basalis (NB) in a ChAT-ChR2(Ai32) mouse: maximum-intensity projection from a 2-photon z-stack through a fixed section. C: image of ChR2-YFP-labeled axons in primary motor cortex (M1) in a ChAT-ChR2(Ai32) mouse: maximum-intensity projection from a 2-photon z-stack through a fixed section. D and E: pyramidal neuron in layer 5B of M1 3 wk after virus injection. Neuron was filled with Alexa Fluor 594 during whole cell recording (D) and surrounding cholinergic axons expressing ChR2-YFP (E). Both images are maximum-intensity projections from 2-photon z-stacks. F: examples of voltage recordings from 4 layer 5B pyramidal neurons at rest. Each voltage response was evoked by stimulation of cholinergic axons by widefield illumination of the slice with a blue LED (stimulus: 10 × 5 ms at 20 Hz; blue bars). Example of slow depolarization includes a preceding hyperpolarization. Examples of slow depolarization and fast hyperpolarization were obtained from virus-injected mice. Examples of medium depolarization and fast depolarization were obtained from ChAT-ChR2(Ai32) mice.