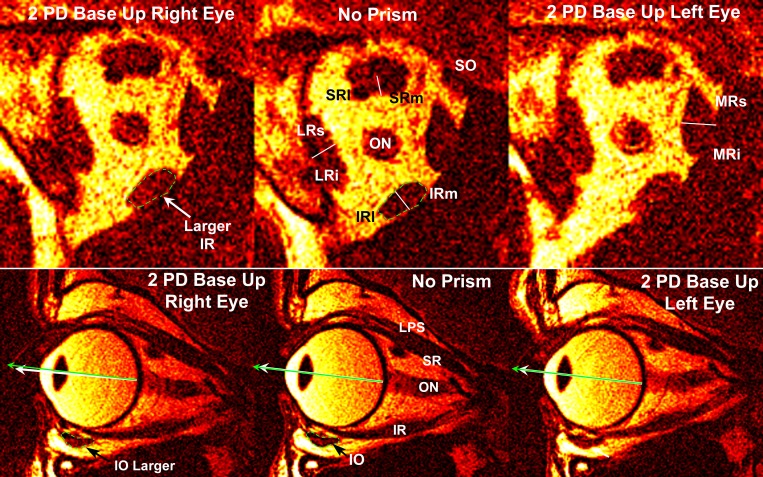
Fig. 1.
Quasi-coronal (top row) and quasi-sagittal (bottom row) magnetic resonance imaging of right orbit of subject viewing binocularly without prism (center column) and during vertical fusional vergence (VFV) with two prism diopter (PD) prism base up (BU) over the right eye (left column) and separately over the left eye (right column). Green arrows indicate visual direction to the target. White arrow at bottom left indicates infraduction of the eye viewing through BU prism. LR, lateral rectus muscle. Rectus cross sections have been divided into presumptive compartments as indicated by the fine white lines. Dotted green outlines of the inferior oblique (IO) and inferior rectus (IR) for the “No Prism” condition have been superimposed upon the corresponding muscles for the “2 PD Base Up Right Eye” condition to illustrate the corresponding small increases in muscle size for this viewing condition. SO, superior oblique; SR, superior rectus; SRl, lateral SR; SRm, medial SR; LRs, superior LR; LRi, inferior LR; IRm, medial IR; IRl, lateral IR; MR, medial rectus; MRs, superior MR; MRi, inferior MR; LPS, levator palpebrae superioris; ON, optic nerve.