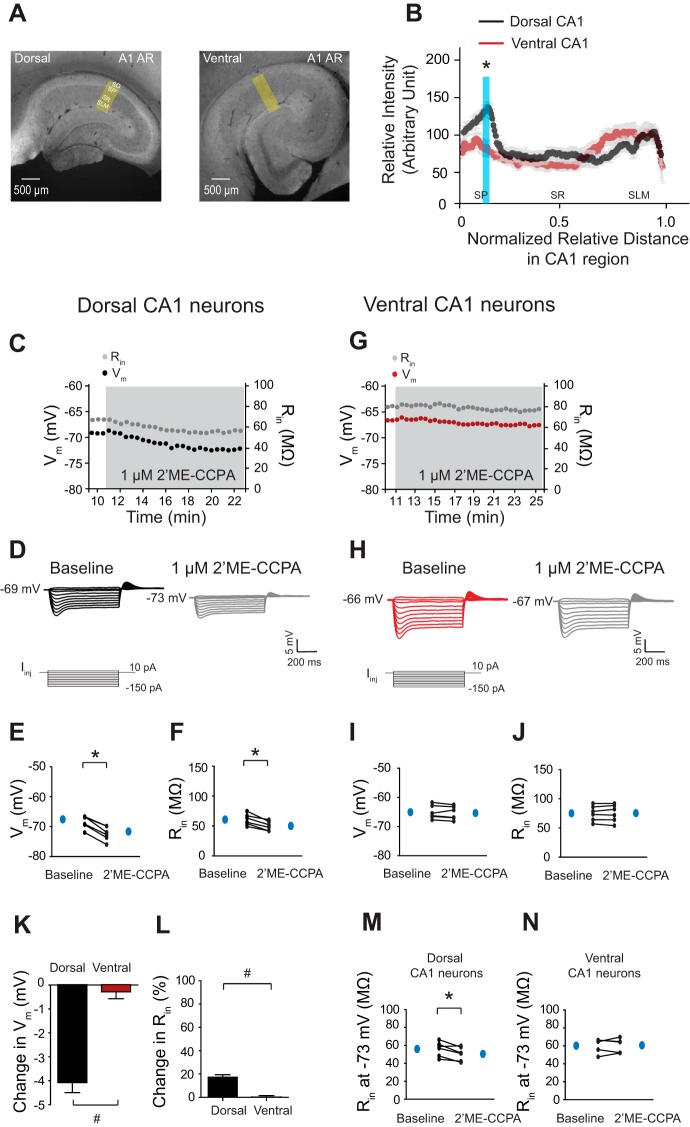
Fig. 7.
A1ARs and their physiological responses predominantly exist in dorsal but not in ventral CA1 neurons. A: representative dorsal and ventral hippocampal slices immunolabeled with antibodies against A1ARs. Yellow boxes depict the region of the slice used for quantification of signal intensity. B: quantification of A1AR protein expression from the perisomatic region to the distal dendritic region of CA1 from the dorsal and ventral hippocampus. The protein expression of A1ARs was highly present in the somatic CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus but not in the ventral CA1 region. The blue shade indicates a significant difference in A1AR protein expression between the dorsal and ventral CA1 region. C and G: time courses of Vm and Rin during 2-chloro-2′-C-methyl-N-6-cyclopentyladenosine (2′ME-CCPA; 1 μM) wash-in experiments in dorsal (C) and ventral (G) CA1 neurons. D and H: representative voltage responses with step current commands at RMP. E and F: dorsal CA1 neurons showed a significant hyperpolarization (E) and a decreased Rin (F) at RMP in the presence of 2′ME-CCPA (1 μM). I and J: ventral CA1 neurons showed no changes in Vm (I) and Rin (J) at RMP after 2′ME-CCPA (1 μM) wash-in. K and L: the changes in Vm (K) and Rin (L) after 2′ME-CCPA (1 μM) application were greater for dorsal CA1 neurons than ventral CA1 neurons. M and N: activation of A1ARs resulted in a significantly decreased Rin at a common Vm (−73 mV) in dorsal (M) but not in ventral (N) CA1 neurons. *P < 0.05; #P < 0.05 vs. ventral group.