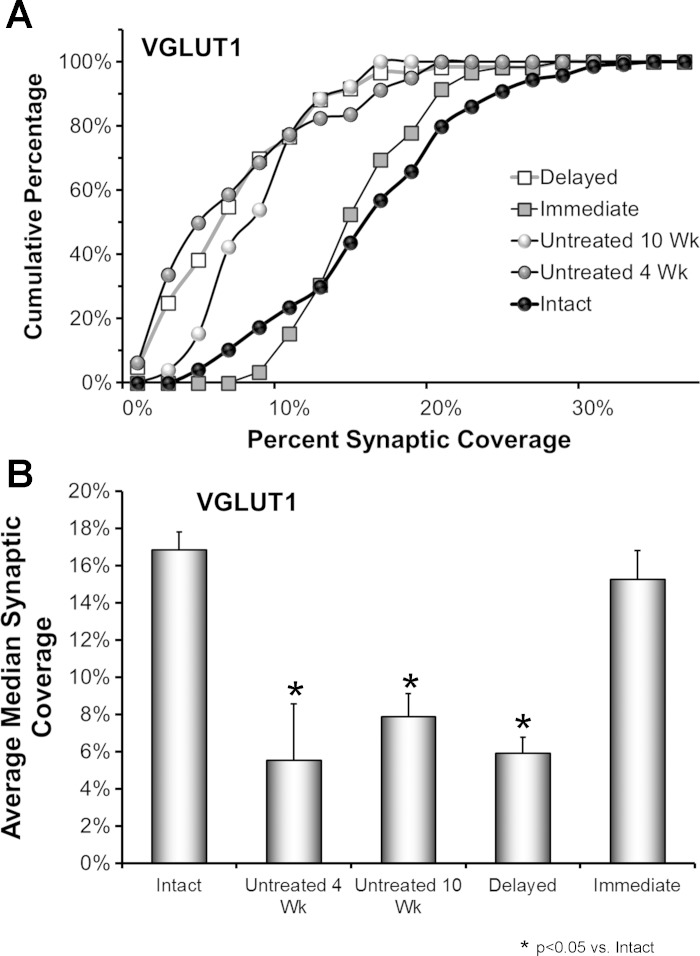
Fig. 3.
The effects of delayed treadmill exercise on synaptic coverage by VGLUT1-IR terminals on motoneurons are shown. A: data from 4 rats in each group were pooled and used to construct cumulative frequency distributions. Results are presented for Untreated animals at 2 different survival times (4 wk and 10 wk, N = 80 cells in each group), and for animals treated with 2 wk of daily treadmill exercise, begun either 3 days (Immediate) or ca. 3 wk (Delayed) after nerve injury (N = 60 cells per group) and examined 10 wk after the initial peripheral nerve transection and repair. Control data are presented from the Intact sides of the 4 rats in the Untreated 10 wk group (N = 80 cells). The values on the X-axis correspond to the percent of the cell perimeter in contact with VGLUT-IR structures in the different cells studied. Values on the Y-axis represent the cumulative frequencies with which the different values were observed. B: the average median (±SE) synaptic coverage by VGLUT1-IR structures is shown for the same groups of rats as in A. N = 4 rats in each group.