Fig. 1.
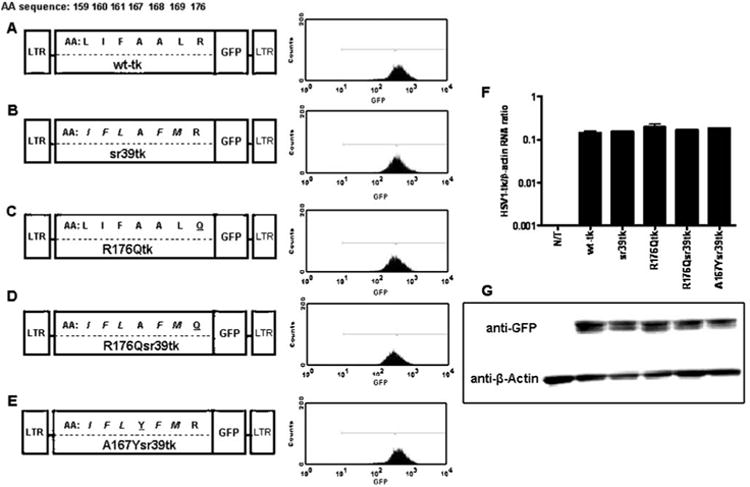
Schematic structure of retroviral vectors for mammalian expression, the amino acid differences between wild-type and different HSV1-tkGFP mutants. a Wild-type HSV1-tkGFP. b HSV1-sr39tkGFP. c HSV1-R176QtkGFP. d HSV1-R176Qsr39tkGFP. e HSV1-A167Ysr39tkGFP reporter genes. Five amino acid substitutions from HSV1-sr39tk are italicized; R176Q and A167Y targeted mutations are underlined. Expression levels were normalized by FACS in transduced U87 cells using a GFP filter set. f Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of HSV1-tk mRNA from non-transduced (N/T) and transduced cell populations normalized by β-actin mRNA levels; values expressed as HSV1-tk mRNA/β-actin concentration ratios. g Western blot analysis of HSV1-tk/GFP (∼72 kDa) and β-actin (∼42 kDa) proteins expression in non-transduced and transduced cell populations using GFP- and β-actin-specific monoclonal antibodies. Blot lines correspond to the cell line names in f
