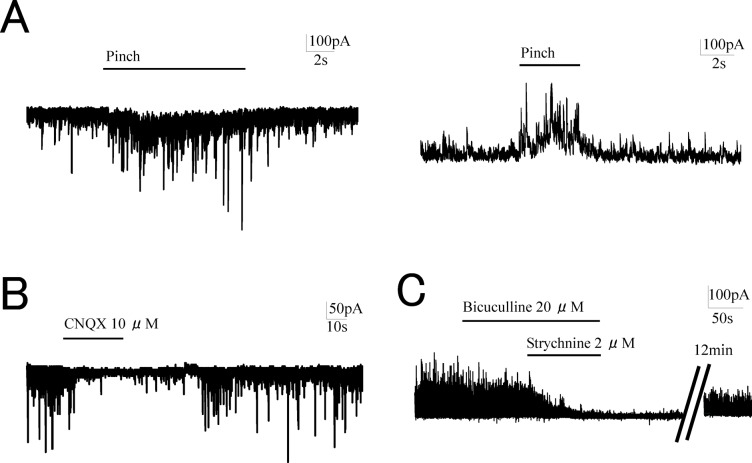
Fig 2. The characteristics of synaptic currents in substantia gelatinosa neurons.
(A) The identification of SG neurons was made by the response of the EPSCs and IPSCs to a pinch stimuli applied to rat hindpaw. (B) The perfusion of CNQX (10 μM) on the spinal cord immediately abolished spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs). (C) Coadministration of bicuculline (20 μM) and strychnine (2 μM) in the perfusion solution diminished spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs).