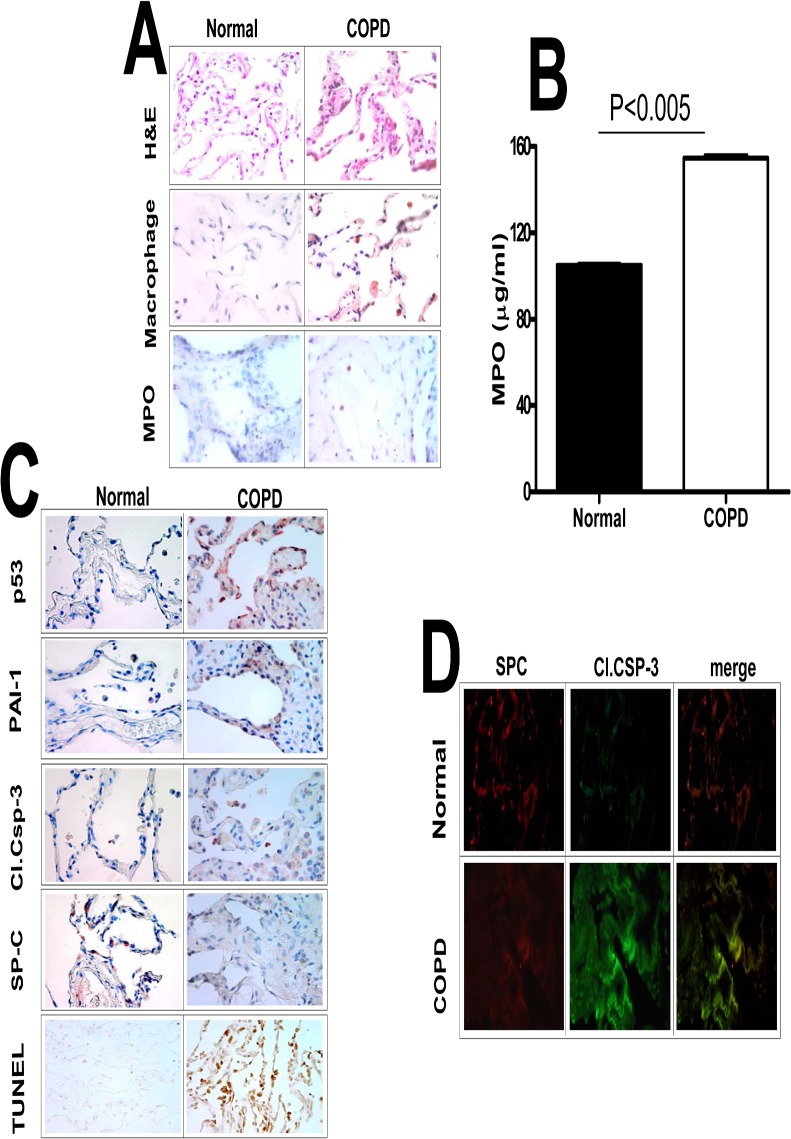
Fig 1. Increased p53 and PAI-1 antigen levels, and AEC apoptosis in the lung tissues of patients with COPD.
(A) Paraffin embedded sections from COPD and histologically “normal” donor lung tissues were subjected to H & E and IHC staining for macrophages and myeloperoxidase (MPO) using specific antibodies. (B) Lung homogenates from COPD (n = 3) and histologically “normal” donor lung tissues from control patients were also tested for MPO activity by colorimetric assay. Data shown in bar graphs are mean ± SD of two independent experiments. (C) The lung sections were also subjected to IHC analysis using anti-p53, anti-PAI-1, anti-active caspase-3 and anti-SP-C antibodies to assess their expression and apoptosis in AECs. Lung sections were also subjected to TUNEL staining to assess apoptosis. (D) Immunofluorescence staining was performed for the above lung sections using anti-SP-C and anti-active caspase-3 primary antibodies and fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies to assess apoptosis of type II AECs. Representative fields from 1 of 3 sections per subject are shown at X 400 magnification.