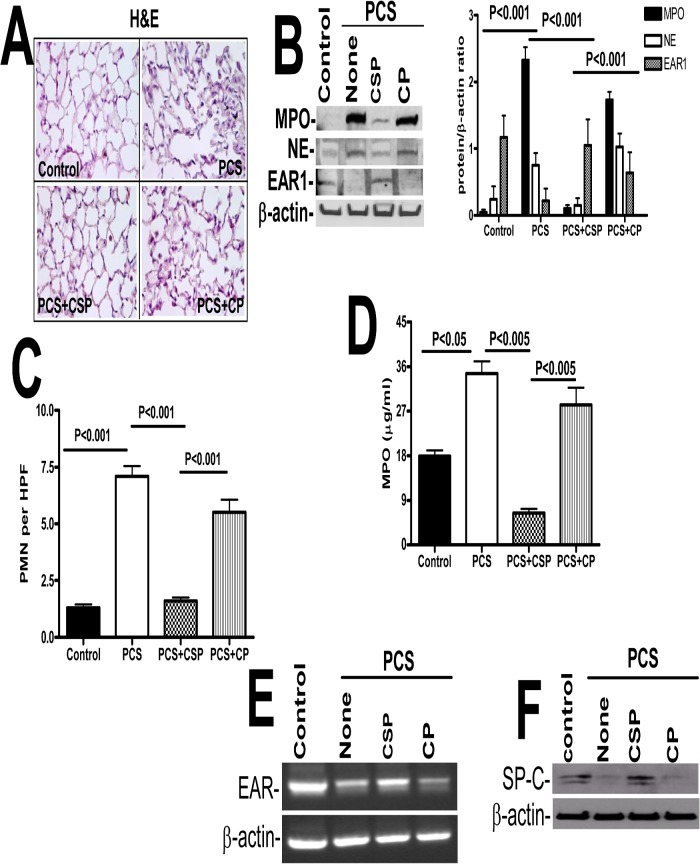
Fig 4. CSP inhibits PCSE-induced induced MPO and neutrophil elastase in mice.
WT mice were exposed to ambient air or PCS as described in the Methods for 5 days per week. After 4 weeks of PCS exposure, mice exposed to PCS were IP injected with or without 18.75 mg/kg body weight of CSP or CP once every week for 4 more weeks. After 20 weeks of PCS exposure, mice were euthanized. (A) Paraffin embedded lung sections from WT mice were subjected to H & E staining. Representative fields from 1 of 3 sections per subject are shown at X 400 magnification. (B) Lung homogenates from these mice were tested for changes in MPO, neutrophil elastase (NE), EAR1 and β-actin by Western blotting. Densities of individual bands normalized against β-actin are shown in a bar graph of two independent experiments (n = 5 mice/group). (C) Lung sections of the mice were subjected to IHC analysis using anti-MPO antibodies. Neutrophils were quantified by counting positive cells in 10 high-power fields (hpf) are shown as bar graph. (D) Lung homogenates from WT mice exposed to ambient air or PCS treated with or without CSP or CP were tested for MPO activity by colorimetric assay. (E) Total RNA obtained from the lungs of these mice were tested for changes in the expression of EAR and β-actin mRNA by RT-PCR. Experiments were repeated at least two times (n = 5 mice/group). (F) Type II AECs isolated from the mice as described above were immunoblotted for SP-C with β-actin as the loading control.