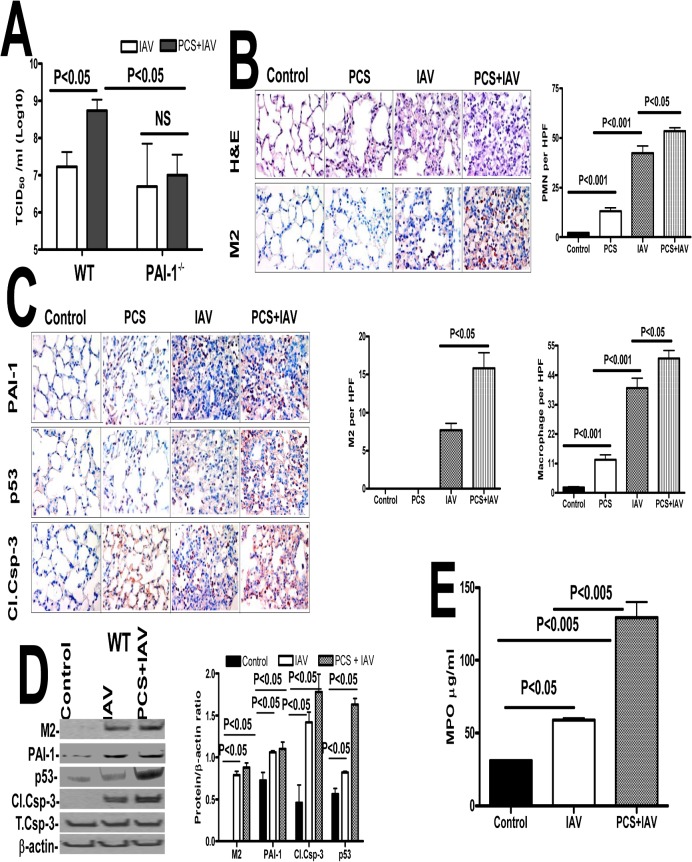
Fig 7. Increased IAV infection in mice with PCSE is associated with augmented p53 and PAI-1 expression, and type II AEC apoptosis.
(A) Mice exposed to ambient air (AIR) or PCS were treated with 50 μl saline or IAV in saline via intranasal instillation. One week after IAV infection, these mice were euthanized. Lungs homogenates were quantified for viral titers using hemagglutination assay. (B) Mice exposed to ambient air (AIR) or PCS were treated with 50 μl saline or IAV in saline via intranasal instillation. One week after IAV infection, these mice were sacrificed. Sections (5 μM) from the inflated lungs were subjected to H & E staining, IHC analysis to detect viral protein M2, neutrophil and macrophage staining using specific antibodies. Representative fields from 1 of 3 sections per subject are shown at X 400 magnification (n = 5 mice/group). The changes in neutrophils, macrophages and M2 levels in the lung sections were quantified by counting positive cells in 10 high-powered fields (hpf) are shown as bar graph. (C) Mice exposed to ambient air or PCS for 19 weeks were treated with 50 μl saline or 0.5 LD50 of purified IAV in saline through intranasal instillation. One week after IAV infection these mice were sacrificed. Lung sections were analyzed for changes in p53 and PAI-1 and active caspase-3 antigen levels by IHC. Representative fields from 1 of 3 sections per subject are shown at X 400 magnification. (D) Lung homogenates were immunoblotted for changes in IAV M2 antigens to assess severity of IAV infection and also for changes in p53 and PAI-1 expression and active caspase-3 for apoptosis. Bar represents ratios in the densities of bands normalized against β-actin levels in the same sample (n = 5 mice/group). (E) Lung homogenates were tested for MPO activity by colorimetric assay which are represented as bar a graph of two independent experiments (n = 5 mice/group).