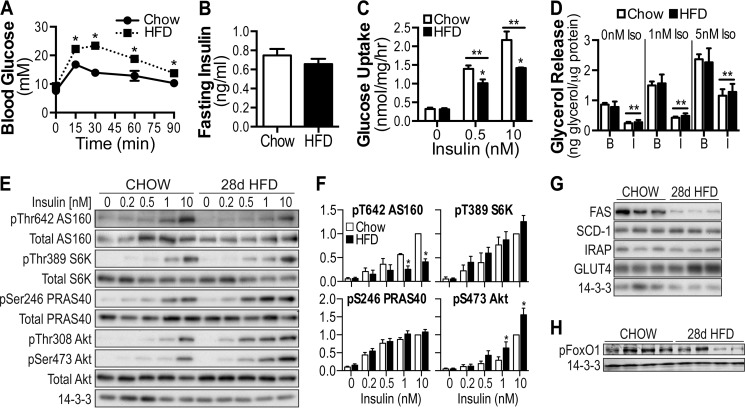
FIGURE 6.
Selective insulin resistance in adipose tissue of high fat-fed mice. 8-week-old C57BL/6J mice were placed on standard chow diet or HFD for 28 days. A, intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests were performed on mice at a dosage of 2 g/kg of body weight. B, fasting insulin was assessed via ELISA following a 4-h fast. C, adipose explants were stimulated with the indicated doses of insulin, and [3H]2-deoxyglucose uptake was determined. D, lipolysis was assessed in the absence and presence of insulin (100 nm) following stimulation with 0, 1, and 5 nm isoproterenol. B, basal; I, insulin. E–G, adipose tissue lysates from explants experiments were immunoblotted using indicated antibodies. H, lysates prepared from white adipose tissue collected from 4-h fasted chow, and HFD mice were immunoblotted using antibodies raised against Ser(P)-256 FoxO1 and 14-3-3. The data are means ± S.E., n = 5–8. *, p < 0.05 versus chow; **, p < 0.05 versus 0 insulin condition. Ins, insulin; Iso, isoproterenol.