Figure 1.
Loss of Elongator Complex in Arabidopsis Interferes with Auxin-Controlled Morphogenesis and Post-transcriptional Regulation of PINs
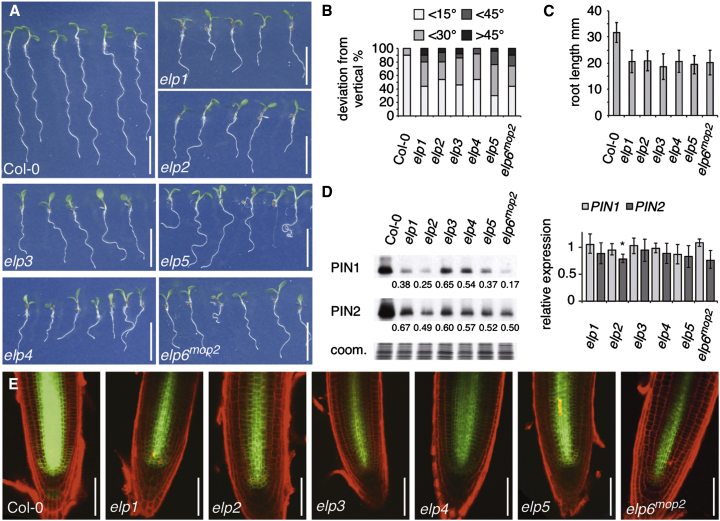
(A) Comparison of wild-type Col-0 and elp mutant seedlings at 7 DAG.
(B) Orientation of primary root growth of Col-0 and elp seedlings at 9 DAG. A total of 50 seedlings were analyzed for each genotype and plotted as percentage of seedlings displaying <15°, <30°, <45°, and >45° deviation from the vertical growth axes.
(C) Comparison of primary root length of Col-0 and elp seedlings at 5 DAG. 20 seedlings were analyzed for each genotype. SDs are indicated.
(D) Quantification of PIN1 and PIN2 protein (left panels) and mRNA (right panels) in Col-0 and elp seedlings at 7 DAG. Relative signal intensities are indicated below (Col-0 = 1); “coom.” displays Coomassie staining of samples used. qPCR performed with Col-0 (= 1) and elp mutants displaying transcript levels of PIN1 and PIN2. SDs from three biological repeats with three technical replicates are indicated (∗Student’s two-tailed t test; p < 0.05).
(E) Comparison of PIN1::PIN1:GFP signals (green) in Col-0 and elp mutant root meristems at 5 DAG. Propidium iodide staining (PI, red) was used for visualizing cell boundaries.
Size bars in represent 10 mm (A) and 50 μm (E). See also Figures S1 and S2.