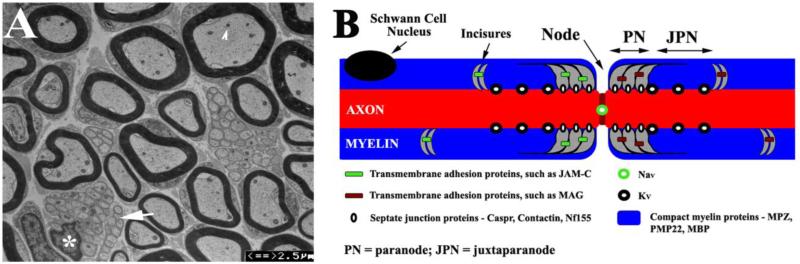
Figure 1.
(A). Transverse section of a 3-month-old mouse sciatic nerve was examined by electron microscopy. Myelinated nerve fibers showed different diameters, which varied positively with myelin thickness. Intra-axonal organelles, such as mitochondria, were visible (arrowhead). Between myelinated nerve fibers, there were Remark bundles (arrow) where a Schwann cell (its nucleus marked by an asterisk) invests a group of nonmyelinated nerve fibers. (B). A diagram illustrates the localizations of proteins on myelinated nerve fibers. Specific subsets of proteins reside in different compartments (node, paranode, juxtaparanode and compact myelin of internode) of the myelinated nerve fiber.