Figure 1.
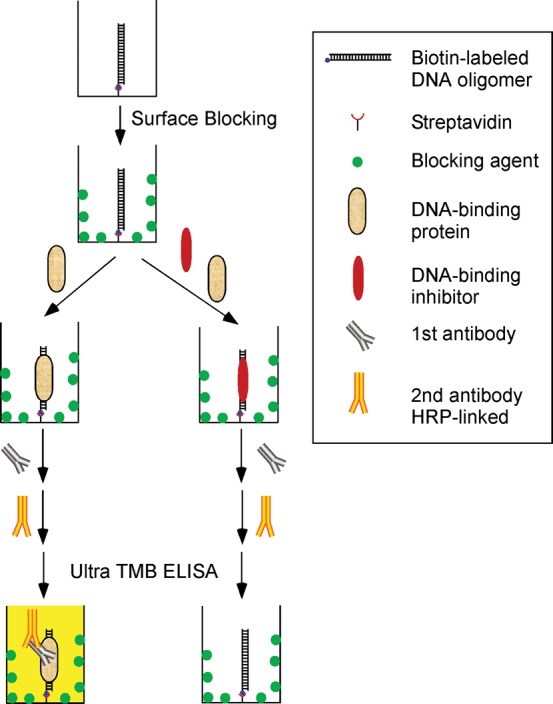
The concept of a high-throughput screening method to identify compounds or proteins targeting protein–nucleic acids interactions. The first step is to link a biotin-labeled oligomer to surface of a multiple-well plate through biotin–streptavidin interaction. After the surface-blocking step, a nucleic acids–binding protein is added to the wells to bind to the oligomer. The compounds or proteins of interest can also be added to the wells to inhibit or enhance the protein binding, which is the basis of the method for high-throughput drug screening. Colorimetric, chemiluminescence or fluorescence methods can be used to detect whether the compounds or proteins inhibit or enhance the binding capacities of the nucleic acids–binding protein.
