Figure 3.
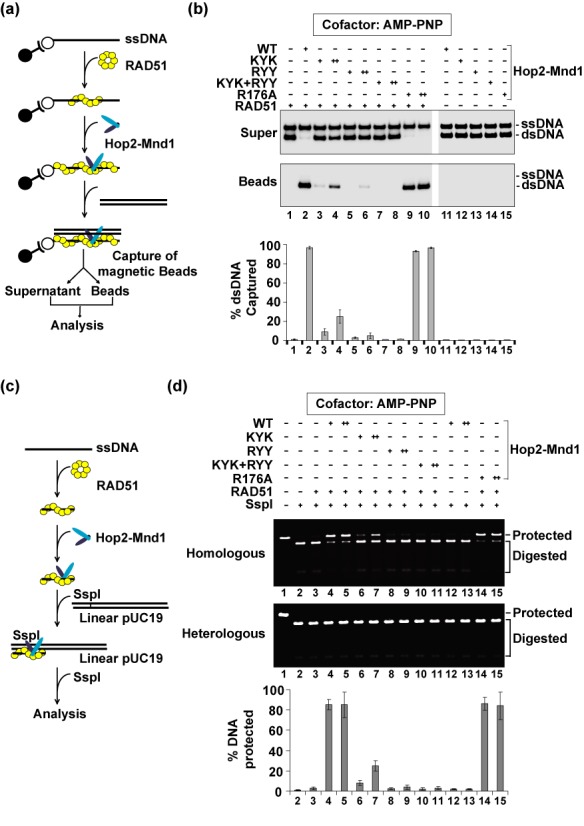
Role of the N-terminal DNA binding domains of Hop2-Mnd1 in duplex DNA capture and synaptic complex assembly. (a) Schematic of the duplex capture assay (13). (b) Wild type (WT) and mutant variants of the Hop2-Mnd1 complex (0.6 or 1.2 μM) were tested for their ability to promote duplex capture with AMP-PNP as nucleotide cofactor. (c) Schematic of the restriction enzyme protection assay to examine synaptic complex formation (12,25). (d) WT and mutant variants of the Hop2-Mnd1 complex (0.48 or 0.96 μM) were tested for their ability to promote synaptic complex formation with AMP-PNP as nucleotide cofactor. In (b) and (d), the mean values ± s.d. from three independent experiments were plotted.
