Figure 1.
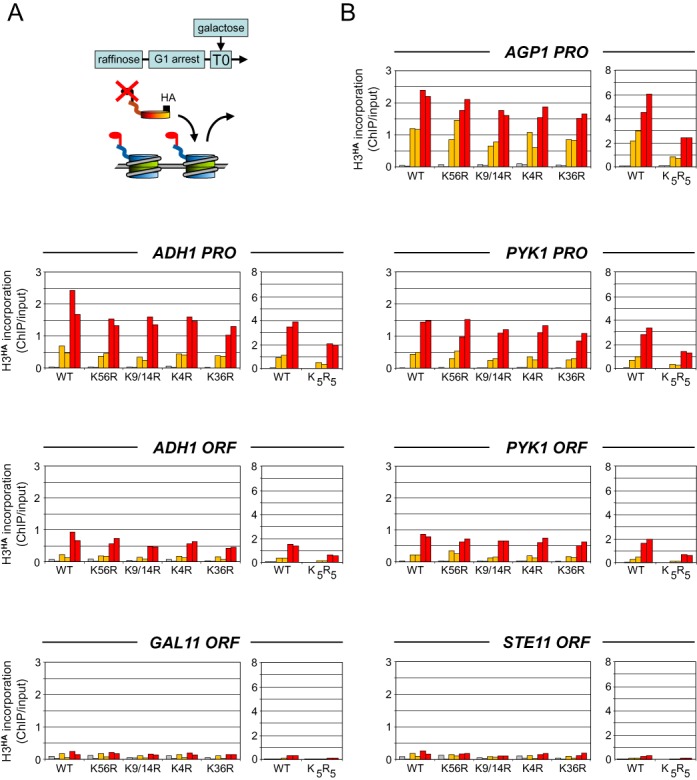
Transcription-dependent incorporation of histone H3 modification mutants in a wild-type chromatin background. (A) Schematic diagram illustrating the experimental approach. Yeast strains expressing a galactose-inducible HA-tagged histone H3 or derivatives with specific N-terminal lysine-to-arginine mutations to prevent their modification were grown overnight in raffinose and arrested in G1 by alpha factor. Expression of H3HA was induced by galactose at T0 (min). Its incorporation into chromatin, which indirectly measures histone exchange (31), was monitored at various time points by quantitative ChIP analysis using antibodies against the HA tag. (B) Time course of incorporation of wild-type H3HA and the indicated modification mutants at the promoter (PRO) and in the coding region (ORF) of the highly transcribed AGP1, ADH1 and PYK1 genes, the weakly expressed GAL11 gene and the inactive STE11 gene. K5R5 carries a K9/14/18/23/27R quintuple mutation. Shown are the amounts of tagged histones detected just prior to (gray bars) and at 30 min (orange bars) and 60 min (red bars) after galactose addition. Data are expressed as the percentage of input DNA recovered. A control western blot for galactose activation of the H3HA proteins is shown in Supplementary Figure S1. Shown are the results of two independent biological experiments.
