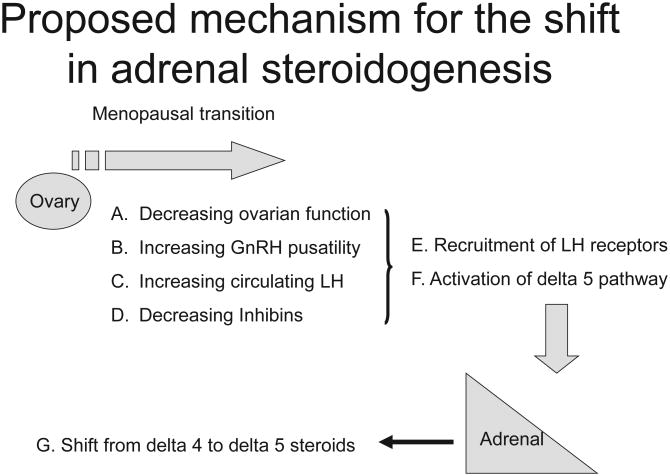
Figure 3.
A proposed mechanistic sequence for the shift in adrenal steroidogenesis during the menopausal transition. The progression of steps involves a decline in ovarian function (A) which leads to increased GNRH pulsatility (B), increasing luteinizing hormone (C) and decreased inhibins (D). In combination these events there is a recruitment of luteinizing hormone receptors in the adrenal cortex (E) and activation of the delta 5 steroid pathway (F). The chronic elevation of circulating luteinizing hormone acting on the activated luteinizing hormone receptors result in a shift from the delta 4 to delta 5 pathway.