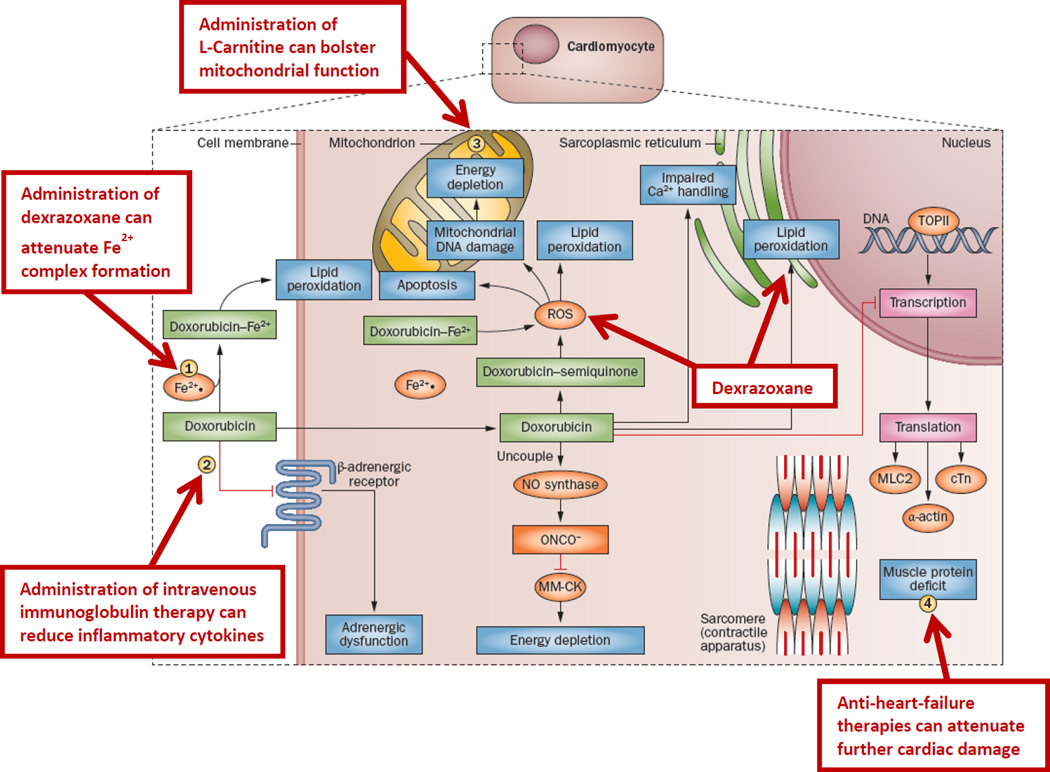
Figure 1. Potential Opportunities for Cardioprotection.
Doxorubicin chemotherapy has a range of effects on cardiomyocytes. It induces lipid peroxidation at the cell and mitochondrial membranes by way of complexing with Fe2+ and induces apoptosis, mitochondrial DNA damage and energy depletion through its production of reactive oxygen species. Furthermore, it impairs Ca2+ processing in the sarcoplasmic reticulum and inhibits the transcription of important muscle elements, weakening the heart muscle. It also downregulates adrenergic receptors and interrupts cell signaling. (1) Administration of dexrazoxane can prevent Fe2+ complex formation. (2) Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy can reduce inflammatory cytokines. (3) L-carnitine can bolster mitochondrial function. (4) Anti-heart-failure therapies, such as angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and β-blockers, can prevent further damage. Abbreviations: cTn, cardiac troponin; MLC2, myosin light chain 2; MM-CK, myofibrillar isoform of the CK enzyme; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TOPII, topoisomerase 2. (Reprinted with permission from Nature Publishing Group [21].)