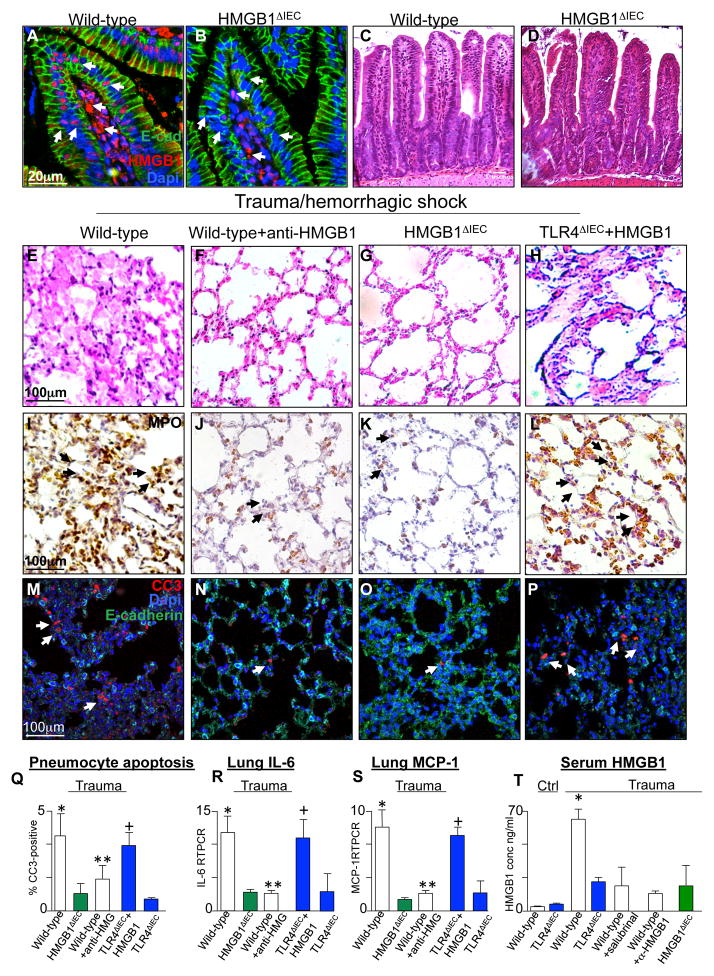
Figure 3. Remote lung injury after trauma requires HMGB1 release from the intestinal epithelium.
A–B: Representative confocal micrographs of the intestinal villi of untreated wild-type (A) and intestinal specific HMGB1 knockout mice (B, HMGB1ΔIEC), stained for HMGB1 (red), E-cadherin (green) and DAPI (blue); arrows show HMGB1 stained nuclei in intestinal epithelium and lamina propria in wild-type mice, but in lamina propria only in the HMGB1ΔIEC mice. C–D: Representative H&E stained histomicrographs showing sections obtained from the terminal ileum of wild type (C) and HMGB1ΔIEC mice (D). E–P: Representative micrographs showing sections of lung from either wild-type (E, I, M), wild-type + exogenous HMGB1 (4 mg/kg, F, J, N), HMGB1ΔIEC (G, K, O), or TLR4ΔIEC + exogenous HMGB1 (4 μg/g, H, L, P) mice that were either untreated or were subjected to trauma/hemorrhagic shock as indicated. Sections were imaged by bright field microscopy and stained for H&E (E–H) or myeloperoxidase (I–L, brown, arrows show MPO-positive cells), or were imaged by confocal microscopy and were stained for cleaved caspase 3 (red, arrows show apoptotic cells), DAPI (blue) or E-cadherin (green) in M–P). Q–R: mean±SEM of percent CC3-positive cells/high power field (Q) and expression of IL-6 (R) and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP1) (S) by qRT-PCR in wild-type, HMGB1ΔIEC or TLR4ΔIEC mice that were subjected to trauma/hemorrhagic in the presence or absence of exogenous anti-HMGB1 or recombinant HMGB1 (4μg/g) as indicated. In both panels, *p<0.05 wild-type vs. HMGB1ΔIEC, **p<0.05 wild-type vs. wild-type + anti-HGMB1, +p<0.005 TLR4ΔIEC vs. TLR4ΔIEC + recombinant HMGB1. All data are mean±SEM; at least 6 animals per group repeated in triplicate. T: Serum HMGB1 by ELISA in mice of the strain indicated subjected to trauma/hemorrhagic shock in the presence of salubrinal (10μM) or anti-HMGB1 as shown. All groups are significantly different from wild-type by ANOVA, p<0.05. Representative of 3 independent experiments.