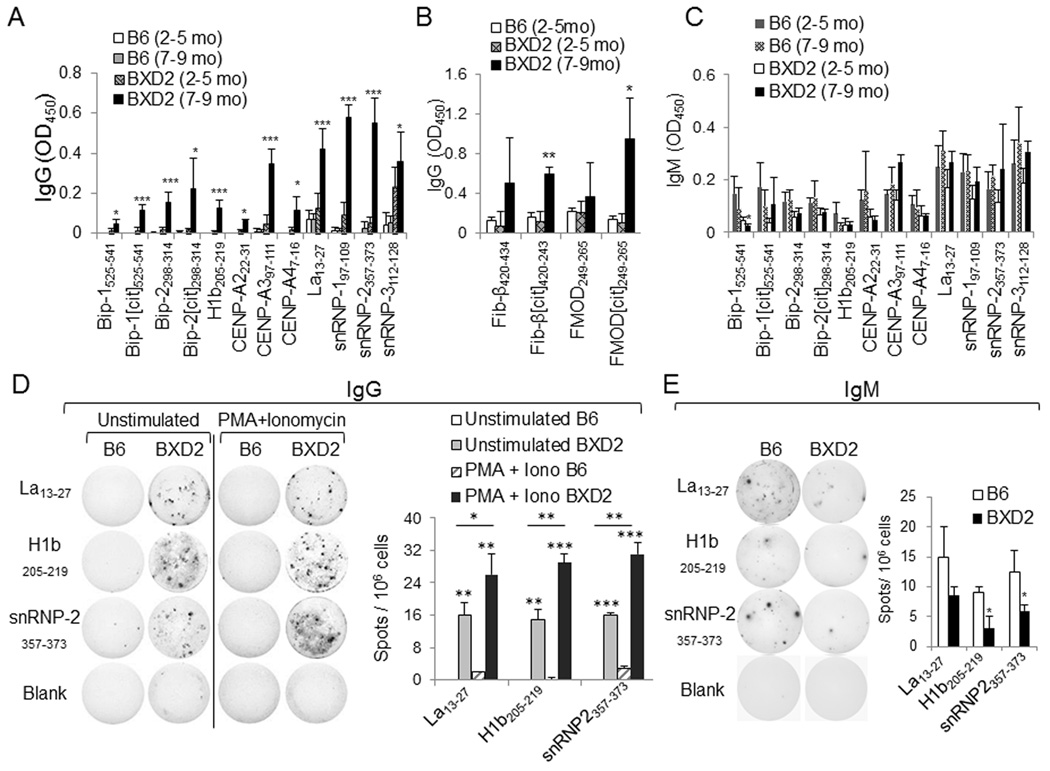
Fig. 3.
Verification of synthesized peptides. (A-C) ELISA of A IgG autoantibodies specific to BiP, histone, centromere, and ribonucleoprotein peptide epitopes; (B) IgG autoantibodies specific to fibrinogen and fibromodulin peptide epitopes, and C IgM autoantibodies specific to BiP, histone, centromere, and ribonucleoprotein peptide epitopes in the sera of B6 and BXD2 mice at the indicated ages. All data are the mean ± SEM of at least four mice per group. (D, E) ELISPOT assay of the D IgG or E IgM isotype autoantibody-producing B cells from B6 or BXD2 mice. Total spleen cells from 5–6 month-old B6 or BXD2 mice were cultured in vitro unstimulated (or stimulated with PMA + ionomycin in the IgG specific ELISPOT) on neutravidin ELISPOT plates coated with Lupus La13–27, histone H1b205–219 or snRNP357–373. Right, mean ± SEM number of D IgG or E IgM autoantibody-forming spots. Results are data from 3–5 mice and at least two independent experiments. For all panels, * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.005 versus control group (normal B6 mice or the indicated comparison).