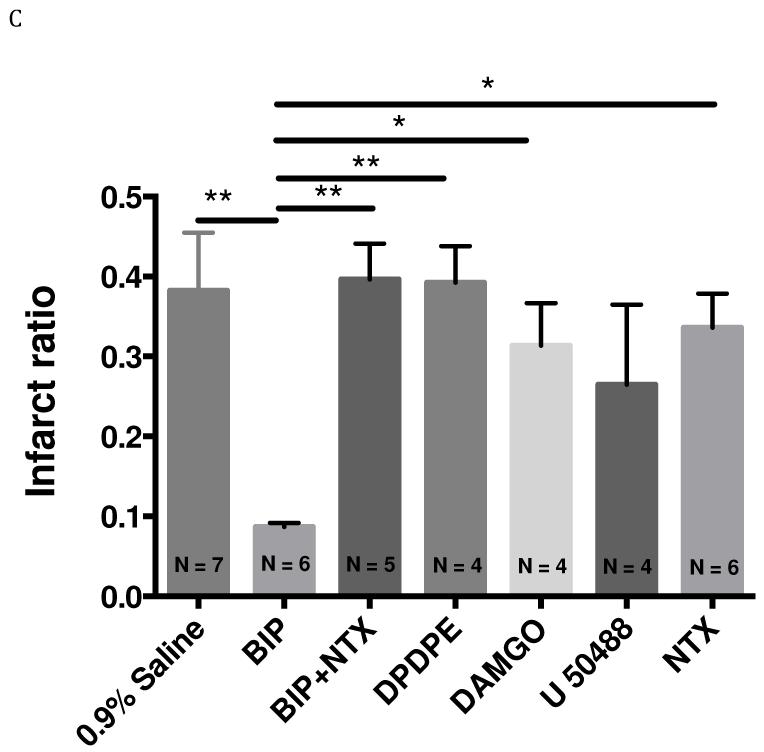
Figure 5.
Effect of intraperitoneal injection of biphalin, selective OR agonists (5 mg/kg, I.P. administrated 10 min after reperfusion), non-selective OR antagonist, naltrexone, (1 mg/kg, I.P. administrated 10 min before the surgery) or vehicle on edema and infarct formation in transient MCAO (60 min occlusion and 24 h reperfusion). A. Representative TTC staining of brains from vehicle and drug -treated mice. B. Brain edema formation in vehicle and drug -treated mice. Biphalin significantly decreased edema ratio (P<0.01) compared to saline treated group. NTX reversed (P<0.05) the effect of biphalin. Compared to selective agonists DPDPE (P<0.001) and DAMGO (P<0.001), biphalin significantly reduced edema ratio. Effect of DPDPE, DAMGO and U50,488 was not statistically significant compared to saline treated group. C. Brain infarct ratio in vehicle and drug-treated mice. Biphalin significantly reduced infarct ration (P<0.01) compared to 0.9% saline treated group. Biphalin showed better neuroprotection in terms of infarct ratio reduction compared to DPDPE (P<0.01), DAMGO (P<0.05) and NTX (P<0.05). NTX reversed (P<0.01) the effect of biphalin. In terms of infarct ration reduction, DPDPE, DAMGO and U50,488 did not show a statistically significant effect compared to vehicle treated group. (*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; numbers indicated in parenthesis in the figure columns donate to the number of experimental animals per group). Mean cerebral blood flow reductions ± SEM in ischemic brain for saline group 80.7 ± 1.24%, biphalin 78.5 ± 0.96%, BIP+NTX 79.7 ± 2.02 %, DPDPE 81.3 ± 2.05 %, DAMGO 79.7 ± 0.83%, U50,488 78.8 ± 1.72% and NTX 76.9 ± 2.01%.