Figure 4. Molecular Mimicry (MM) Theory of Autoimmune Disease.
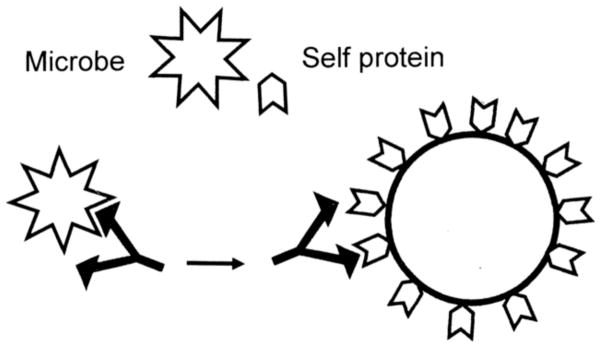
Many microbial proteins mimic host proteins resulting in epitope mimicry. Antibodies or T cells activated against a microbial epitope may therefore share weak affinity for the corresponding host epitope so that infection may induce autoimmune disease directed at cells displaying the epitope mimic [28, 97–102, 135].
