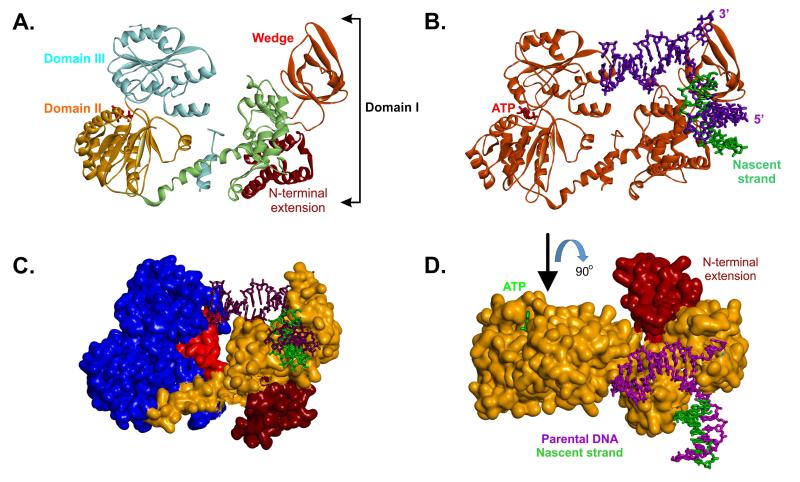
Figure 3. Domain organization of the RecG DNA helicase.
(A), a ribbon diagram showing the three domains of RecG (details in the text). The positions of the wedge sub-domain and N-terminal extension, present in T. maritima RecG but not E.coli, are indicated. (B), a ribbon diagram of RecG (orange) bound to a model fork substrate. The position of the ATP sandwiched between domains II and III is highlighted in red. (C), T. maritima RecG is represented as a Connelly surface. The N-terminal extension is coloured brown; the wedge and linker region are coloured orange and the helicase domains are blue. The TRG motif is coloured in red. (D), T. maritima RecG is represented as a Connelly surface and is coloured orange. The N-terminal extension is indicated. The view of the protein is rotated 90° relative to that in panel B.