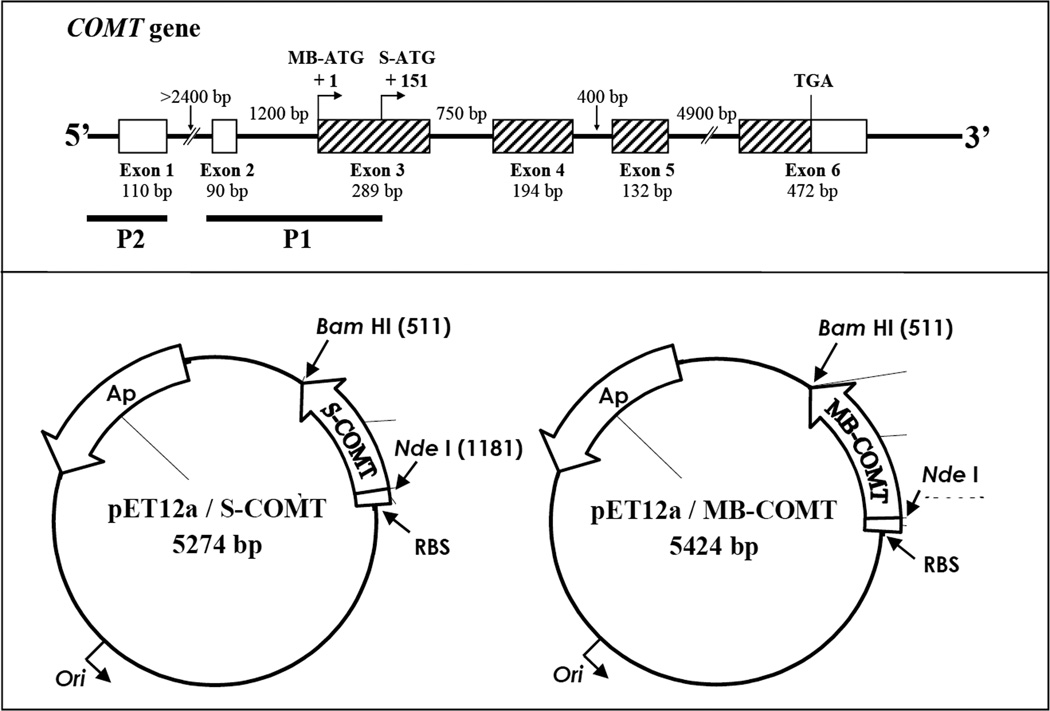
Figure 1.
Upper panel: Structure of the human COMT gene. The boxes represent exons and the thin lines between the boxes represent introns. The hatched boxes indicate protein-coding regions. The size of each exon and intron is as indicated. The positions of the initiation codons for transcription of S-COMT and MB-COMT mRNAs are indicated as S-ATG and MB-ATG. The two known promoters, P1 and P2, are shown by black bars. Note that the P1 promoter for transcritpion of S-COMT overlaps with the initiation codon and part of the coding sequence for MB-COMT. Lower panel: Construction of the pET12a/S-COMT and pET12a/MB-COMT expression vectors based on the vector pET12a. The S-COMT or MB-COMT cDNA was cloned into the NdeI and BamH I sites of pET12a to form the pET12a/S-COMT or pET12a/MB-COMT expression vectors. Each of the expression vectors was under the control of the T7 promoter and lacO-operator. Expression was induced by addition of 0.5 mM isopropylthio-β-D-galactoside.