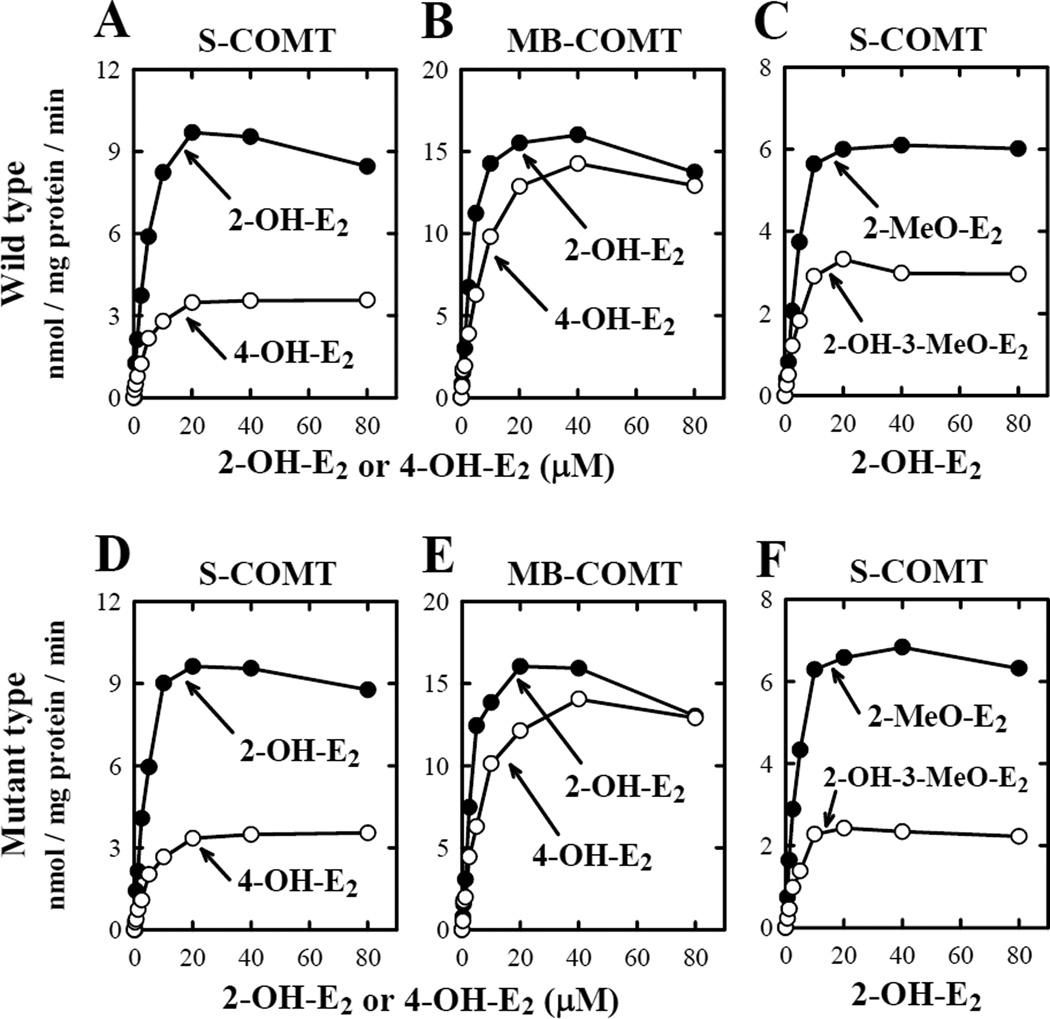
Figure 3.
Relationship between catechol estrogen concentrations and their rate of O-methylation by wild-type human COMTs (A, B and C) and mutant human COMTs (D, E, and F). The upper right panel (C) showed the rate of 2-O-methylation and 3-O-methylation of 2-OH-E2 catalyzed by the wild-type S-COMT, and the lower right panel (F) showed the rate of 2-O-methylation and 3-O-methylation of 2-OH-E2 by mutant S-COMT. The incubation mixture consisted of 10 different concentrations (0, 0.31, 0.63, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 µM) of each substrate, 1.2 mM MgCl2, 100 µM AdoMet (containing 0.5 mCi [methyl-3H]AdoMet), 1 mM 1,4-dithiothreitol, and the recombinant COMT protein (at 16.2 µg/mL for S-COMT or 17.1 µg/mL for MB-COMT). The incubations were carried out at 37°C for 15 minutes. Note that the rate of its total methylation was based on liquid scintillation counting of the radioactivity extracted with ethyl acetate. The rates for its 2-O- and 3-O-methylation (C and F) were determined by using HPLC that separately quantified the amount of 2-methoxyestradiol (2-MeO-E2) and 2-OH-E2 3-methyl ether (2-OH-3-MeO-E2) formed. Each value is the mean of duplicate measurements.