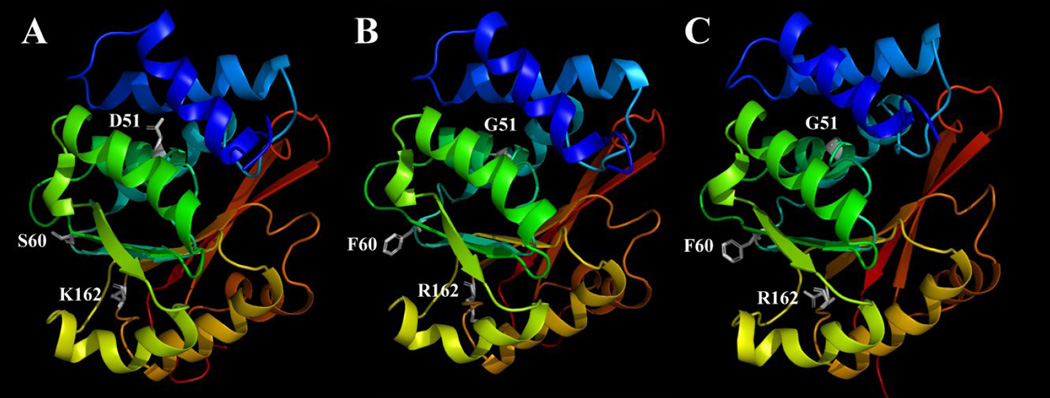
Figure 6.
The wild-type human S-COMT (A), the D51G/S60F/K162R mutant S-COMT built according to the homology model of the wild-type human S-COMT (B) or according to the crystallographic structure of the rat S-COMT (PDB code: 1VID) (C). The figure is drawn with the PyMOL software. Secondary structures are shown with colored ribbons with blue for N-terminus and red for C-terminus. AdoMet, Mg2+ and substrates are not included in this model. The amino acids at mutation sites (D51, S60 and K162 for wild-type S-COMT and G51, F60 and R162 for mutant S-COMT) are shown in white sticks. Hydrogens are omitted from the amino acids.