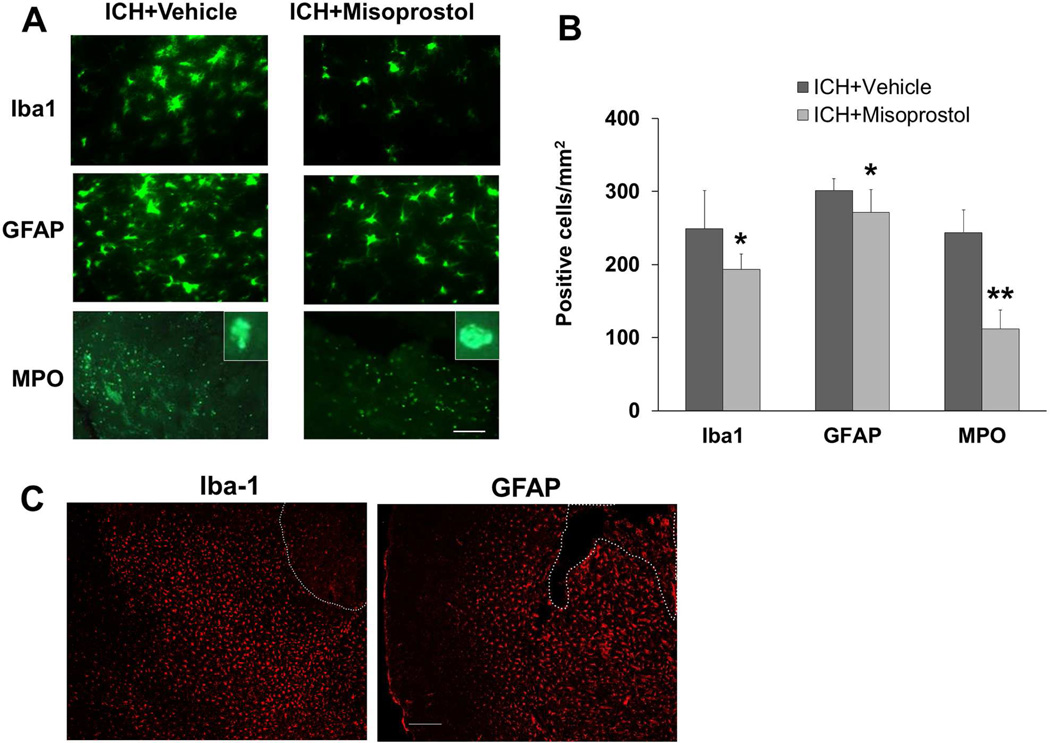
Fig. 4.
Misoprostol treatment decreases cellular inflammatory response in the collagenase-induced ICH model. (A) Activated microglia/macrophages (Iba1-immunoreactive cells), reactive astrocytes (GFAP-immunoreactive cells), and infiltrating neutrophils (MPO-immunoreactive cells) were evident around the injury site on day 3 after ICH. Insets represent MPO-positive cells at higher magnification. Scale bar = 40 µm. (B) Misoprostol treatment reduced the number of activated microglia/macrophages, activated astrocytes, and infiltrating neutrophils (n=8 mice/group, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, t-test). (C) Activated microglia/macrophages (amoeboid, Iba1-immunoreactive cells) and reactive astrocytes (GFAP-immunoreactive cells) were distributed equally around the hematoma on day 3 after collagenase-induced ICH. The dashed white lines indicate lesion edge. Scale bar = 50 µm. All values are means ± SD.