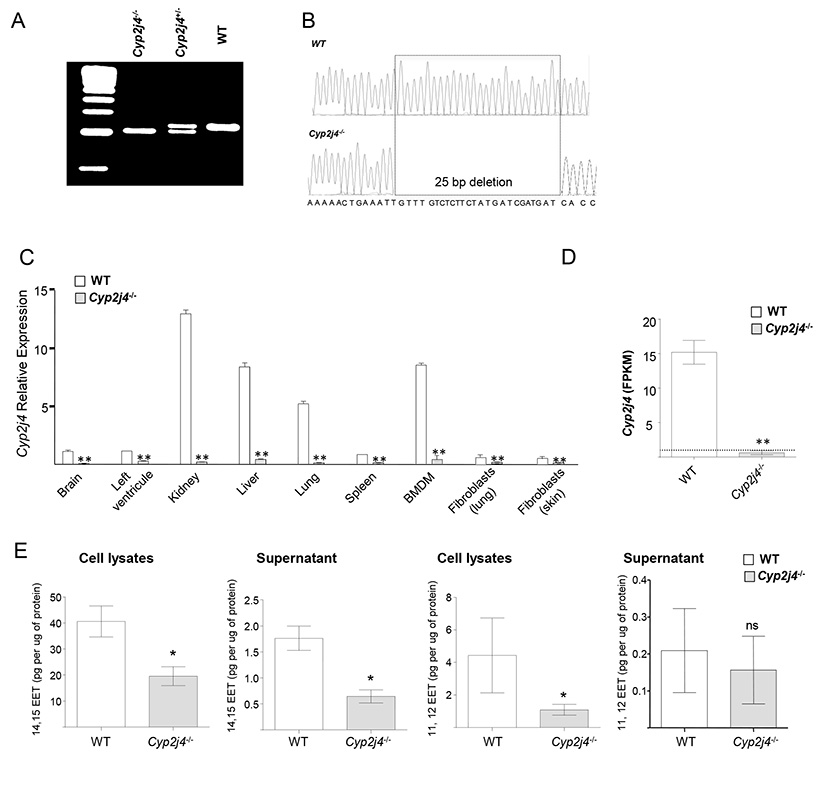
Figure 2.
Targeted gene deletion of Cyp2j4 in the rat. (A) ZFN-mediated gene targeting resulted in a deletion of 25bp in rat exon 4. (B) Sanger sequencing chromatograms of rat Cyp2j4 exon 4 shows the 25 bp deletion that creates a frameshift in the genomic sequence of Cyp2j4. The coding sequence resulting from the frameshift deletion (see Supplementary Figure 1) generates a premature stop codon at exon 6 of Cyp2j4. (C). ZFN-mediated genetic deletion in rat Cyp2j4 results in a marked reduction in Cyp2j4 expression in major tissues and bone marrow derived macrophages when assessed by qRT-PCR. Error bars indicate SEM; *, P<0.001 (D) RNA-sequencing in bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs) of Cyp2j4−/− and WT rats confirms the markedly reduced Cyp2j4 expression in Cyp2j4−/− BMDMs. FPKM values are shown for Cyp2j4. **, P<0.001. FPKM = 1 is shown with a dotted line. (E) 11,12- and 14,15-EETs measurements in the supernatants and cell lysates of WT and Cyp2j4−/− BMDMs. *, P<0.05; ns, non-significant.