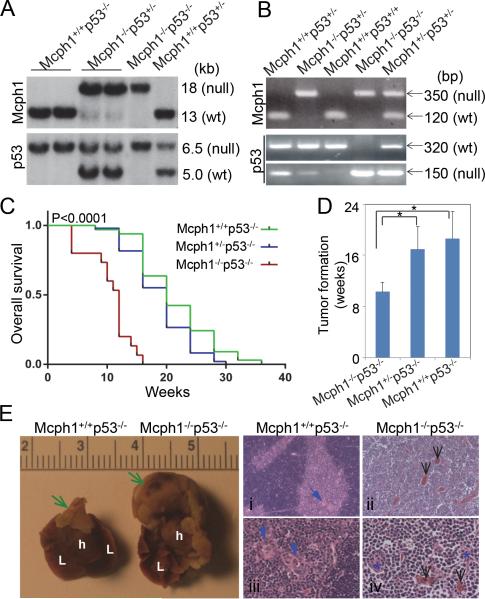
Figure 2. Mcph1 deficiency accelerates tumorigenesis in the absence of p53.
(A) Southern blot analysis of mice genotyping. For Mcph1, the sizes of the WT and null alleles are 13 kb and 18 kb, respectively; for p53, the sizes are 6.5 kb (WT) and 5.0 kb (null). (B) PCR-based genotyping of mice. For Mcph1, the sizes of the PCR products are 350 bp (null) and 120 bp (WT); for p53, the sizes are 320 bp (WT) and 150 bp (null). (C) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of Mcph1+/+p53−/− (n=33), Mcph1+/−p53−/− (n=49), and Mcph1−/−p53−/− (n=15) mice. (D) Average tumor onset in Mcph1+/+p53−/−, Mcph1+/−p53−/−, and Mcph1−/−p53−/− mice. * P<0.05. (E) Representative thymic lymphoma in Mcph1−/−p53−/− mice. (Left) Gross images of normal thymus and thymic lymphoma (scale=cm). Green arrows indicate normal thymus (in Mcph1+/+p53−/−) or thymic lymphoma (in Mcph1−/−p53−/−). L, lung; h, heart. (Right) Histological characterization of thymus or thymic lymphoma. Tissues were cut from normal thymus (Mcph1+/+p53−/−) or thymic lymphoma (Mcph1−/−p53−/−), and stained with H&E. Normal thymus is composed of a dark-staining basophilic cortex and a light-staining eosinophilic medulla (i, iii). Normal cortex contains numerous densely packed lymphocytes, and the medulla has fewer lymphocytes and more thymic corpuscles (blue arrows). However, there is no definite cortex and medulla structure in thymic lymphoma from Mcph1−/− p53−/− mice (ii, iv), and the entire region is composed of densely packed lymphocytes and infiltrated with more blood vessels (black arrows). Thymic corpuscles are almost disrupted and infiltrated with more lymphocytes (blue asterisks in panel iv).