Figure 3.
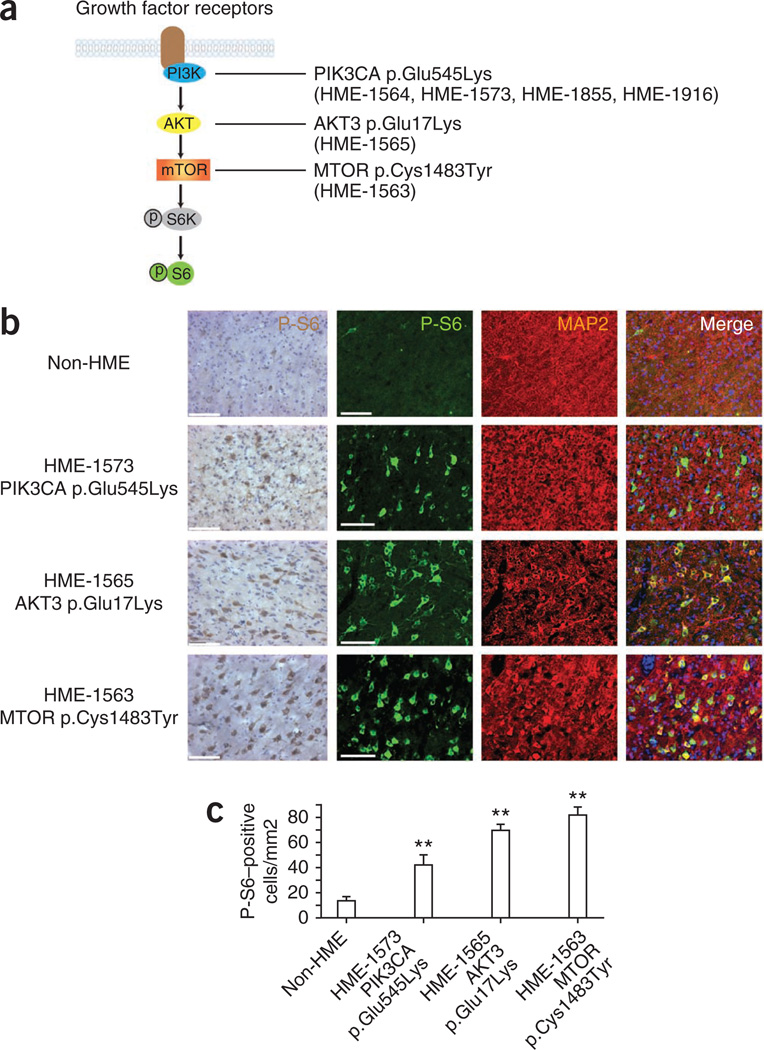
The de novo mutations identified in HME correlate with hyperactive mTOR signaling. (a) Schematic of the PI3K-AKT3-mTOR pathway and downstream phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 kinase (P-S6K) and phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 (P-S6). (b) HME pathological samples show an increased percentage of cells with positive staining for P-S6 and MAP2. Left P-S6, biotin-streptavidin DAB staining; right, P-S6, fluorescence-conjugated staining. MAP2 was used to identify neurons. Scale bars, 100 µm. (c) Quantification of P-S6–positive cells from 5–7 representative cortical areas per case. **P < 0.01 (relative to non-HME samples, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest, n > 50 cells per region). Error bars, s.e.m.