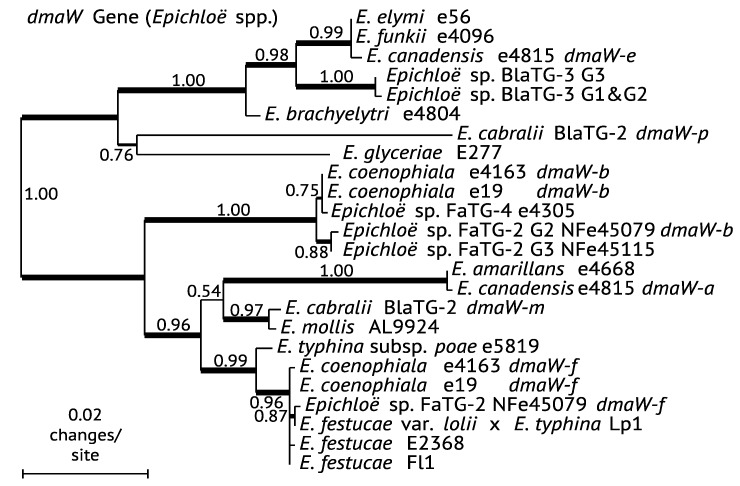
Figure 8.
Phylogeny of dmaW genes of Epichloë strains. The phylogenetic tree was inferred by maximum likelihood on a nucleotide alignment of coding sequences. Methods are as in Figure 3. The dmaW alleles are distinguished in hybrids that possess more than one copy with a letter that refers to the ancestral progenitor (a = E. amarillans, b = E. baconii-related Lolium associated Epichloë subclade, e = E. elymi, f = E. festucae, m = E. mollis-related and p = E. typhina subsp. poae. The dmaW gene of E. inebrians has been omitted in this analysis because the gene and EAS locus is more similar to that of P. ipomoeae than to those of other Epichloë species (see Figure 3).